Due to the strong global demand for industrial robots, various industrial robot companies have increased their production in China. Kuka, the German subsidiary of China’s home appliance giant Midea Group, will build two factories in China and plan to increase its production capacity in China to four times the current level by the end of 2019. Due to rising labor costs and the strengthening of manufacturing, China’s demand for industrial robots has exploded, and China is rapidly emerging as a “robot factoryâ€. KUKA Expands Production Capacity in China On November 30, Stefan Lampa, CEO of KUKA's robotics business, accepted an interview with the Japan Business News. In addition to Germany, KUKA also has a factory in Shanghai, China. First, the second plant will be put into operation in Shanghai in January 2018, and the annual production capacity will be increased to 25,000 times the current level. Later, by the end of 2019, a new workshop will be built in Guangdong to increase the annual production capacity in China to 50,000 units, which is currently four times. The amount of investment has not been announced, but it is expected to be around 10 billion yen. Stefan Lampa stated that "I hope to acquire the automotive industry's robot demand in Shanghai and acquire the robot and electronics industry's robot demand in Guangdong". After the new plant is put into operation, it will export to other Asian countries in addition to China. It also plans to continue to increase the production capacity of its German factories (currently with an annual production capacity of 40,000 units) and strives to increase the total annual production capacity to more than 100,000 units after 2020. Rapidly growing Chinese robot market KUKA is affiliated with Midea Group in 2017. As a condition of the acquisition, U.S. promises to retain KUKA's existing management layer, and maintain the independence of KUKA's operations until 2023. Stefan Lampa stated that "China is a big country and it is very difficult to develop the Chinese market from scratch. The United States has a vast sales network in China and will expand sales and services with the support of the United States." Stefan Lampa said that after 2023, "the United States sells home appliances and other products to consumers, and the division of labor of KUKA's products for robots and other products will not change." Deny the United States will be involved in the operation of KUKA. On the other hand, plans to cooperate with Midea in the development of new technologies "have begun consultations on cooperation in the field of artificial intelligence (AI)." According to the forecast of the International Robot Alliance, the global sales of industrial robots will increase by 77% compared with 2016. Among them, China's sales are expected to soar to 2.4 times. In China, due to the rising labor costs and the ageing trend of low births caused by the one-child policy, the shortage of manpower in the manufacturing frontline is outstanding. In addition, the Chinese government's policy of strengthening manufacturing has also prompted companies to accelerate the introduction of industrial robots. Japanese Industrial Robot Manufacturers Lag Behind China is the "biggest market" for industrial robots, and Japanese companies are constantly launching offensives. Yaskawa Electric not only began to increase production at its Chinese factories, but also formally cooperated with Midea Group. It is intended to put the nursing rehabilitation robots jointly developed by both parties on the market and devote themselves to the export of factory automation systems. Yasuhara Electric, president of Yaskawa Electric, said: "In the future, we will continue to cooperate with our partners." Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Fujio also successively decided to increase production at the Chinese factory. Fanuc, which only produces robots in Japan, plans to invest 63 billion yen to build a new robot factory in Ibaraki Prefecture. The Swiss company abb plans to "increase the global production capacity of industrial robots by more than two times in the next 1-2 years." According to reports, ABB has factories in Europe and China, and plans to continue to increase production capacity throughout the country. On the other hand, although Chinese companies are also stepping up their efforts to absorb technology, Governor Hashimoto Yasuhiko of the Robotics Business Center of Precision Machinery Co., Ltd., executive director of Kawasaki Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., believes: “The gap between the strengths of Japanese and European companies in recent years will not be different. Zoom out." In Chinese companies, the number of small and medium-sized manufacturers has increased dramatically. Abb robots business global president PerVegardNerseth thinks: "(the intensified competitive result) will lead to enterprise integration, and finally there may be only a few companies survived." Vertical Dip Centronic Connector
Vertical Dip Centronic Connector.
Current Rating:5A Vertical Dip Centronic Connector ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.pcbsocket.com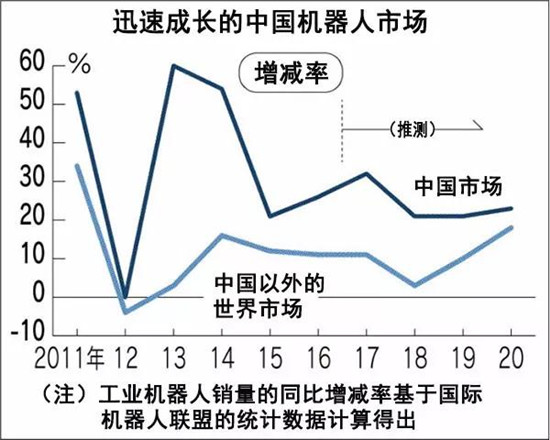
Dielectric Withstanding Voltage:1000V for one minute
Insulation Resistance:1000MΩ Min.(at 500V DC)
Contact Resistance:35mΩ Max.
Temperature:-55°C to +105°C