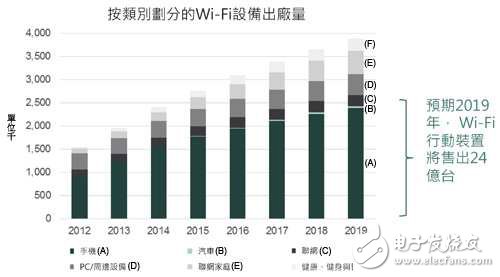
Wi-Fi Aware will break the market for Bluetooth dominates the wearables market. The Wi-Fi Alliance has released a new Wi-Fi Aware technology, adopting the P2P transmission mode, and it is not necessary to connect the devices to each Other through the Wi-Fi core network. It is expected to reverse the stereotype of the Wi-Fi standard. Impression, and then meet the needs of wearable device design, so that Bluetooth Smart is no longer unique. Wi-Fi Aware is a strong player in the design of the wearable device battlefield. The Wi-Fi Alliance (Wi-Fi Alliance) has introduced the Wi-Fi Aware certification program to lead the Wi-Fi standard to low-power point-to-point (P2P) connectivity, and can be combined with device-to-device (D2D), proximity sensing ( Neighbor Awareness) The new development of the application. As Wi-Fi Aware overcomes the inherently high power consumption of standard power consumption, Wi-Fi expands into the wearable market and will be just around the corner, and it is expected to divide the market share of Bluetooth Smart. Kelly Davis-Felner, vice president of marketing for the Wi-Fi Alliance, said Wi-Fi Aware provides instant, dynamic, and enhanced user experience through the user's environment. Kelly Davis-Felner No need to rely on GPS/Internet Wi-Fi Aware shocked debut Kelly Davis-Felner, vice president of marketing for Wi-Fi Alliance, said that the new Wi-Fi Aware standard allows devices to instantly explore nearby Wi-Fi without a Wi-Fi access device or gateway. Fi devices, applications, and related information. In response to this disruptive Wi-Fi standard, the alliance officially launched the Wi-Fi Aware certification program in June 2015 to verify whether Wi-Fi solutions from various vendors are highly efficient and explore proximity services. Because Wi-Fi Aware can send and receive a small amount of information before the connection is established to facilitate two-way communication between devices, and without the need to connect to the Internet, this feature can help users discover the surrounding information and equipment, so they can fully meet the wear. Device design requirements, market penetration will gradually increase (Figure 2). 2012-2019 Wi-Fi device shipment analysis Davis-Felner believes that as the Wi-Fi Aware ecosystem matures, more proximity service application ideas can be introduced for smart watches/glasses. With support for future operating systems, application developers will be able to leverage Wi-Fi Aware to create new experiences and accelerate the mobile and social services market. In the past, neighboring technologies did not rely on “neighborhood perception†but relied on location information (GPS or community website punch record). The data must be transmitted to the cloud first, and other users can get relevant information, so that not only is there no immediateness, but it is also impossible. Know if there are friends nearby. In response, Davis-Felner analyzed that Wi-Fi Aware creates more direct and practical context-aware capabilities, providing personalized applications with continuous scanning of surrounding information, predictive actions, sending service notifications, and selecting preferences notifications. It is connected by P2P architecture, does not need to use the Cellular Network, Wi-Fi or GPS connection to transmit signals, and can be used in the general Wi-Fi network, instantly switch to Wi-Fi Direct, 802.11 High-speed transmission mode such as n/ac; in other words, this technology provides a context-aware solution that works both indoors and in a signal-intensive environment. Breaking Bluetooth's Outstanding Situation Wi-Fi Aware Marching Wear With Wi-Fi Aware moving closer to the P2P connection and adding more D2D design elements, the Wi-Fi standard is expected to continue to flourish under the wave of the Internet of Things, and to attack new applications in the Blue Ocean, including retail Beacon, mobile advertising, Game search and indoor positioning, etc., as well as wearable device application opportunities that are always available but not available. It is worth noting that the power consumption problem has always been a natural danger to block Wi-Fi from entering the smart bracelet/watch and glasses applications. With the Wi-Fi Aware standard, the transmission power consumption is equivalent to the general P2P communication technology. Wi-Fi will be able to enter the wearable application smoothly, and divide the leading Bluetooth Smart market share. Davis-Felner pointed out that as of now, five wireless chip manufacturers such as Intel, MediaTek, Raychem, Broadcom and Marvell have passed Wi-Fi Aware certification; system-side design verification It is also in full swing. It is expected that mobile phones, tablets and other terminal products will be released first during the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) from the end of this year to next year. As for the wearable market, it will be the next development opportunity for Wi-Fi. In addition to the above-mentioned big manufacturers, China Core chip makers such as Rockchip are also actively investing in R&D, and are optimistic about Wi-Fi Aware combined with low-power Wi such as 802.11b or 802.11ah. -Fi standard solution. Davis-Felner stressed that this shows Wi-Fi's full range of connectivity support capabilities, as well as its long-lasting technical value, which is expected to complement Bluetooth's lack of audio and video transmission and IP network design. Wi-Fi Aware has undergone several major changes to achieve low-power networking. The first is the new Media Access Control (MAC) layer protocol, which monitors network-wide devices with extremely low power consumption and supports small amounts of bidirectional data transmission such as location information and sensor readings. Secondly, the standard enhanced device synchronization and software access point (SoftAP) mechanism can form a group network for devices operating at the same frequency to directly perform D2D communication. Wi-Fi Aware uses the same underlying architecture as the well-known Wi-Fi standard such as 802.11a/b/g/n/ac, so it can also operate in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, providing proximity network aware services at any time; once there is a large amount of data The demand is switched to Wi-Fi Direct or other traditional Wi-Fi standard mode, which combines low power consumption with high frequency wide connection efficiency. Davis-Felner revealed that Wi-Fi Aware will move toward Sub-GHz and 60GHz, and support the 802.11ah and 802.11ad standards to expand the application landscape. Guangzhou Etmy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.gzdigitaltalkie.com