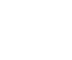
The Internet of Things without security is not an Internet of Things! This has become the basic consensus of everyone in the Internet of Things era. According to statistics, by 2020, there will be 50 billion devices connected to the Internet of Things in the world. Considering the diversity of interconnected communication links and cloud deployments, it is conceivable to maintain the complexity of the security of such a large network system. Some analysts pointed out that 83% of the attacks targeting the Internet of Things are targeted at edge devices, and the largest group of tens of billions is the most unpredictable security in the Internet of Things. "Short board". [ Figure 1: In the security attack against the Internet of Things, a large number of terminal devices have become the main target] More deadly, in the eyes of hackers, edge devices are not their ultimate target. They will use the edge device as an attack interface and become a convenient "gate" for invading the Internet of Things. In this regard, Shijian company senior product manager Terence Li said: So what kind of edge device is a safe IoT node? Some people have summarized the basic elements of their security as "CIA." Confidentiality: Data stored or being sent should be visible only to the licensor; Integrity: Messages sent should not be modified before reaching the destination; Authenticity: It can be assured that "the sender of the message is the claimed person." In order to achieve the goal of "CIA", it is common practice to use a key or a private key as a unique part of the verification identification tag, and to manage the storage and communication of these keys to ensure the security of the system. Although there are many security technologies that can meet the above requirements, developers will still find it difficult to implement them. There are two reasons for this. First, edge devices are often very "simple" and it is difficult to equip "security" with redundant resources. Any security strategy needs to balance computing power, memory, power, cost and more. Second, developers lack targeted, easy-to-use "tools" to solve this problem efficiently. Terence Li, senior product manager at Shijian, said: [ Figure 2: ATECC508A works with the microprocessor to achieve the safety requirements of the edge device "CIA"] ATECC508A supports both Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) and Elliptic Curve Key Exchange (ECDH). Simply add an ATECC508A to the IoT edge node to easily and efficiently implement confidentiality, integrity and authentication mechanisms. The ATECC508A uses a single bus or I2C bus communication with a small number of pins, a minimum package size of only 2mm × 3mm, and a standby sleep current of less than 150 nanoamps. So with a small cost and resource budget, you can add it to your edge devices. ATECC508A receives the input provided by the processor, performs calculations internally and returns calculation results such as signature, authentication, session key, etc., and does not leak the calculation method during the whole process. A high quality True Random Number Generator (TRNG) helps to successfully prevent transactions from being played back. Internal serial numbers help ensure the uniqueness of the key, while large-capacity counters can be used to track the authentication process. In addition, to guard against adjacent attacks and physical attacks, the ATECC508A has been specially designed—the entire chip is covered with a serpentine metal pattern that prevents internal signal release from being detected externally and provides visual impairments that prevent the attacker from opening the package to the chip. Internal observation and detection operations. At the same time, the device protection case is connected to the rest of the circuit. If the protection case is broken, the chip will no longer operate, in case the attacker obtains the key by detecting the circuit node. Terence Li, senior product manager of Shijian Company, concluded that: With the tools of ATECC508A, developers can immediately build a "security door" for the edge of the Internet of Things . [ Figure 3: ATECC508A can be easily configured in production ]
Networking Keystone Jacks.China Cat5e Coupler Jack,Keystone Jack Short Body manufacturer, choose the high quality Cat5e Jack Short,Keystone Jack Unshield, etc, included keystone jacks for CAT6A, CAT6, CAT5E, and CAT3
Keystone jacks are snap in modules used to mount low voltage electrical connectors into a keystone wall plate, patch panel, face plate or surface mount box.
Our Keystone Jacks are available in 10 different colors for easy color-coded installations.
RJ45 port editing Cat5e Coupler Jack,Keystone Jack Short Body,Cat5e Jack Short,Keystone Jack Unshield ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.atkconnectors.com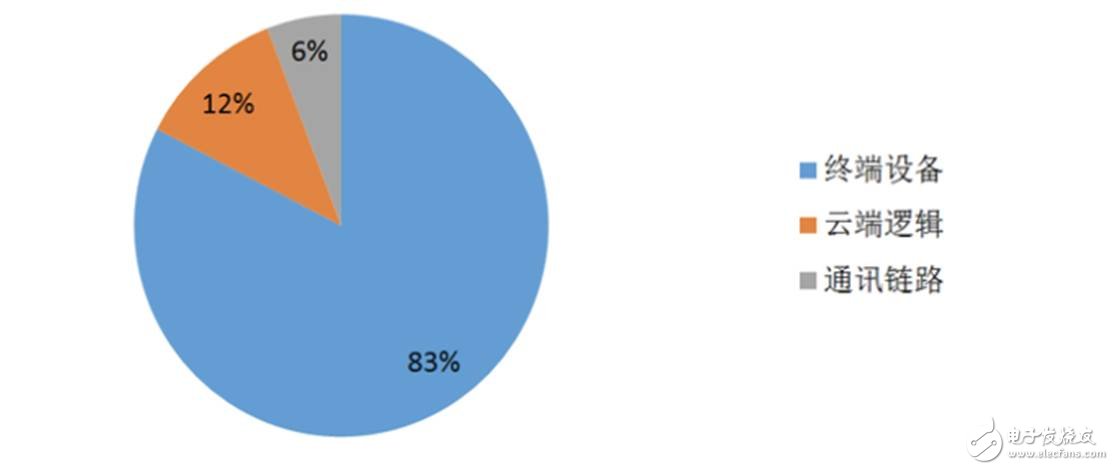
 Once an intruder enters (or spoofs) an IoT node into the IoT network, the security of the entire network becomes more vulnerable. They can steal important databases, undermine normal workflows, access them through cloud services, and control the operation of the nodes themselves, which is hard to estimate. Therefore, the security protection of Internet of Things edge devices is gradually becoming the highlight of IoT development. In short, we need to add a “security door†to the edge devices of the Internet of Things to keep possible security threats out of the door. Once an intruder enters (or spoofs) an IoT node into the IoT network, the security of the entire network becomes more vulnerable. They can steal important databases, undermine normal workflows, access them through cloud services, and control the operation of the nodes themselves, which is hard to estimate. Therefore, the security protection of Internet of Things edge devices is gradually becoming the highlight of IoT development. In short, we need to add a “security door†to the edge devices of the Internet of Things to keep possible security threats out of the door.
Once an intruder enters (or spoofs) an IoT node into the IoT network, the security of the entire network becomes more vulnerable. They can steal important databases, undermine normal workflows, access them through cloud services, and control the operation of the nodes themselves, which is hard to estimate. Therefore, the security protection of Internet of Things edge devices is gradually becoming the highlight of IoT development. In short, we need to add a “security door†to the edge devices of the Internet of Things to keep possible security threats out of the door. Once an intruder enters (or spoofs) an IoT node into the IoT network, the security of the entire network becomes more vulnerable. They can steal important databases, undermine normal workflows, access them through cloud services, and control the operation of the nodes themselves, which is hard to estimate. Therefore, the security protection of Internet of Things edge devices is gradually becoming the highlight of IoT development. In short, we need to add a “security door†to the edge devices of the Internet of Things to keep possible security threats out of the door. 
 The good news is that such 'tools' are now available! This is the cryptographic component - it is integrated into the edge device, not only can be used as a hardware crypto accelerator instead of the main processor to complete the complex encryption and decryption algorithm, but also ensure that the key involved in the encryption operation must be stored in a hidden protection. In the hardware, ensure that the key is 'transparent' invisible in software or unprotected hardware. ATECC508A, the latest addition to Microchip's family of cryptographic components, is the most iconic of its kind.
The good news is that such 'tools' are now available! This is the cryptographic component - it is integrated into the edge device, not only can be used as a hardware crypto accelerator instead of the main processor to complete the complex encryption and decryption algorithm, but also ensure that the key involved in the encryption operation must be stored in a hidden protection. In the hardware, ensure that the key is 'transparent' invisible in software or unprotected hardware. ATECC508A, the latest addition to Microchip's family of cryptographic components, is the most iconic of its kind. 
 The ATECC508A supports configuration during production, and the configuration can be easily accomplished using a simple module to ensure that keys and signature certificates are securely inserted into the cryptographic component. This configuration process can be performed by Microchip or by an authorized dealer such as Excelpoint to provide technical support and convenience to the user.
The ATECC508A supports configuration during production, and the configuration can be easily accomplished using a simple module to ensure that keys and signature certificates are securely inserted into the cryptographic component. This configuration process can be performed by Microchip or by an authorized dealer such as Excelpoint to provide technical support and convenience to the user. 

1. Origin:
2. The name RJ stands for the registered jack and is the USOC (universal service ordering codes) code of bell system. USOC is a series of registered sockets and their wiring mode, which are developed by bell system to connect the user's equipment to the public network. FCC regulations control the application of this purpose. The FCC (Federal Communications Commission) issued a document on behalf of the U.S. government to specify RJ11.
3. RJ11 is the common name of the connector developed by Western Electric Co. Its shape is defined as a 6-pin connecting device. Originally called wexw, where x means "active", contact or needle. For example, we6w has all six contacts, numbered from 1 to 6. The we4w interface only uses four pins, the outermost two contacts (1 and 6) are not used, and we2w only uses the middle two pins. For RJ11, the information source is contradictory. It can be a 2 or 4-core 6-pin connector. What's more confusing is that RJ11 is not only used to represent the 6-pin connector, it also refers to the 4-pin version.
4. RJ45 and RJ11: different standards, different sizes
5. Due to the different sizes of the two (RJ11 is 4 or 6-pin, RJ45 is an 8-pin connection device), it is obvious that the RJ45 plug cannot be inserted into the RJ11 socket. However, it is physically feasible (RJ11 plug is smaller than RJ45 jack), which makes people think that they should or can work together. It's not. It is strongly recommended not to use RJ11 plug for RJ45 socket.
â’ because RJ11 is not internationally standardized, its size, insertion force, insertion angle, etc. are not in accordance with the international standard connector design requirements, so interoperability cannot be guaranteed. They even cause damage to both. Since the RJ11 plug is smaller than the RJ45 socket, the plastic parts on both sides of the plug will damage the metal pin of the inserted socket.
RJ - 45 port is our most common port, it is our common twisted pair Ethernet port
Because twisted pair is mainly used as transmission medium in Fast Ethernet, RJ-45 port can be divided into 10Base-T network RJ-45 port and 100base TX network RJ-45 port.
Among them, the RJ-45 port of 10Base-T network is usually identified as "eth" in the router, while the RJ-45 port of 100base TX network is usually marked as "10 / 100btx". This is mainly due to the fact that most products of Fast Ethernet router still adopt 10 / 100Mbps bandwidth adaptive.
The left figure shows the RJ-45 port of 10Base-T network, while the right figure shows the RJ-45 port of 10 / 100base-tx network. In fact, the two RJ-45 ports are exactly the same in terms of the port itself, but the corresponding network circuit structure in the ports is different, so they can not be connected casually.
Definition of RJ45 interface pin signal
Ethernet 10 / 100Base-T interface:
1 TX + tranceive data +
2 TX - tranceive data -
3 RX + receive data +
4 N / C not connected
5 N / C not connected
6 RX - receive data
7 n / C not connected
8 N / C not connected
Ethernet 100base-t4 interface:
1 TX_ D1 + tranceive data +
2 TX_ D1 - tranceive data
3 RX_ D2 + receive data +
4 BI_ D3 + bi directional data +
5 BI_ D3 bi directional data
6 RX_ D2 - receive data
7 BI_ D4 + bi directional data +
8 BI_ D4 bi directional data
Note: RJ45 interface adopts differential transmission mode, TX + and TX - are a pair of twisted pair, which can reduce interference when twisted together.