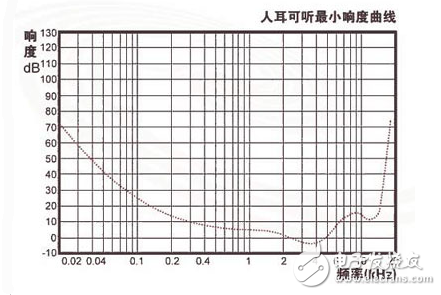
Equalizer A component that corrects the amplitude and frequency characteristics and phase frequency characteristics of a transmission channel. A sine wave with a frequency f is sent to the transmission channel, and the characteristic that the amplitude ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage varies with f is called the amplitude frequency characteristic, which is referred to as the amplitude frequency characteristic; the phase difference between the output voltage and the input voltage varies with f. It is called the phase frequency characteristic and is called the phase frequency characteristic. The signals transmitted by various transmission channels are generally composed of components of different frequencies. In the signal band, if the amplitude-frequency characteristic of 1 channel is a constant value; 2 the characteristic of phase φ varies with f is a straight line, which can be written as ¢(f)=2πft+θ, t is a constant; 3θ (called phase cut) is equal to nπ, n=0, ±2, ±4, . . . , the signal waveform is transmitted without distortion. Condition 1 causes different frequency components to have the same output input amplitude ratio after transmission, and conditions 2 and 3 have the same time delay. However, the actual channel often does not meet the above conditions, and thus the signal is distorted. If the distortion exceeds the allowable amount, the equalizer is used to correct the channel characteristics. The requirements for equilibrium are related to the nature of the signal. Since the human ear is not sensitive to the phase, only the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the channel are required when transmitting the analog telephone signal. When transmitting a TV signal, the amplitude and phase frequency characteristics of the channel are required, otherwise the image is distorted. When the digital signal baseband is transmitted, the amplitude and phase frequency characteristics are required, because the waveform distortion causes inter-symbol interference and increases the bit error rate. When the digital signal carrier is transmitted, the phase cut in the phase-frequency characteristic of the channel is not required. This is because the phase reference is not required when receiving the digital FM signal, and the phase reference can be solved by the carrier recovery circuit when receiving the digital phase-modulated signal. Thus, only carrier frequency characteristics and delay frequency characteristics are required for carrier transmission. The role of the equalizer is to adjust the strength of the signal at different frequencies. Sound as a wave has three elements: amplitude, frequency, and phase. The amplitude determines the size of the sound, and the frequency determines the level of the sound. The actual sound is often not a single frequency wave, but a wave of various frequencies is superimposed, thus forming a distinctive sound. y = Asin(wt+fi)+A0 (single frequency sound wave description) y = A1sin(w1t+fi1) + A2sin(w2t+fi2) + . . . (actual sound wave description) The difference in sound is that the acoustic signals of different frequencies have different intensities. The equalizer is implemented according to this principle. The equalizer automatically separates signals of different frequencies and takes different degrees of magnification or reduction to change the sound. At present, the equalizer has both hardware direct implementation (such as the SAA7709 hardware Equalizer) and software implementation (such as thousands of silent). Of course, in principle, there can be an equalizer for processing an analog signal or an equalizer for processing a digital signal. The equalizer generally divides the frequency range (20Hz-20KHz) that can be heard by humans into multiple frequency bands, and performs different degrees of amplification or reduction (gain or negative gain) on the acoustic signals of different frequency bands. If thousands of thousands of silent, it is divided into 10 frequency bands. The SAA7709 hardware equalizer has 20 hardware units. When using 2X10 mode, the sound signal can be divided into 10 frequency bands (secTIon), while in 4x5 mode, it can be divided into 5 frequency bands (secTIon). In audio equipment, an equalizer is an electronic device that can separately adjust the amount of electrical signal amplification of various frequency components. By adjusting the electrical signals of various frequencies to compensate for the defects of the speaker and the sound field, compensating and modifying various sounds. Source and other special effects, the equalizer on the general mixer can only adjust the three-stage frequency electrical signals of high frequency, intermediate frequency and low frequency respectively. Strictly speaking, the equalizer should be used to correct the sound according to the frequency response curve of the sound. That is to say, the frequency response curve of the sound is not a horizontal straight line, but in order to restore the sound, we can adjust the original by the equalizer. The curve becomes a straight line. But most of my friends don't have this condition. I don't know the frequency response curve of headphones or earphones, so we can only adjust according to our own hearing. First take a look at the role of each part of the equalizer segmentation: 1. 20Hz--60Hz part This promotion can give a strong feeling to the music, giving people a very loud feeling, such as thunder. It is a powerful and powerful feeling in music. If the elevation is too high, it will be turbid, resulting in poor definition, especially for low-frequency response and low-frequency audio equipment. 2. 60Hz--250Hz part This is the low-frequency structure of music, which contains the basic sounds of the rhythm part, including the main sound of the pitch and rhythm sounds. Its ratio to the high-pitched tone constitutes the balance of the tone structure. Raising this section will make the sound full, and excessive boost will make a rumble. Attenuating these two segments will make the sound thin. 3. 250Hz--2KHz part This section contains the low-frequency harmonics of most instruments, and if you increase too much, the sound will be like the sound in the phone. Excessive elevation of 600Hz and 1kHz will make the sound like a horn. If the 3kHz is raised too much, the speech recognition tone will be masked, that is, the articulation is unclear, and the lip sound "mbv" is difficult to distinguish. If you increase the 1kHz and 3kHz excessively, the sound will have a metallic feel. Since the human ear is sensitive to this frequency band, this segment is usually not adjusted, and excessively increasing this segment will cause hearing fatigue. 4. 2KHz--4kHz part This frequency is an intermediate frequency. If it is raised too high, it will cover up the speech recognition tone, especially if the 3kHz boost is too high, it will cause hearing fatigue. 5. 4kHz--5KHz part This is a frequency band with a sense of presence that affects the clarity of sounds such as languages ​​and instruments. Raising this frequency band makes people feel that the distance between the sound source and the listener is a little closer; if the attenuation is 5 kHz, the distance of the sound will be farther; if it is raised by 6 dB at around 5 kHz, the sound of the whole mixed sound will be made. The power is increased by 3dB. 6. 6kHz--16kHz part This band controls the brightness, macro brightness and sharpness of the tone. Generally speaking, raising these segments makes the sound loud, but it is not clear. It is impossible to cause the tooth to be too heavy. When the sound is attenuated, the sound becomes clear, but the sound is not loud. The equalizer can also be set according to the curve of the door limit, so that the ear can feel the sound most easily, so the most natural best! As shown below, we increase the number of DBs for low and high frequencies. This allows the low frequency and high frequency to be naturally felt by the ear, which means that the best EQ setting should match the curve. The CD is a good record of the edited source signal when recording. The sound has been adjusted at the time of CD production, so we can think that no compensation is needed. Mp3 is not the same. When compressing, there will be losses in the high and low frequencies. In general, the loss is at both ends, and the intermediate frequency is largely retained. So the approach I took was to adjust by comparing CD and mp3 file playback. Ejector Header Connector,Ejectors Header Smt Type Connectors,Ejectors Four Row Foot Type Connector,Ejector Wire To Board Connector Shenzhen Hongyian Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.hongyiancon.com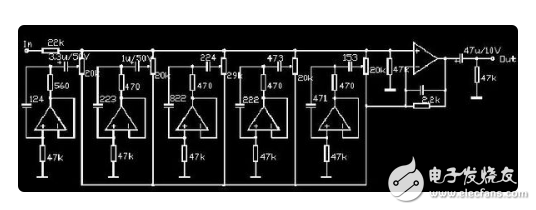
Analysis of the working principle of the equalizer
Principle of equalizer