Dell Inspiron Series,dell insprion,dell insprion 15,dell inspiron 15 3510 S-yuan Electronic Technology Limited , https://www.laptoppalmrest.com
The working principle of the common class D power amplifier (PWM power amplifier): the PWM power amplifier can only accept analog audio signals. The triangle wave generated by the internal triangle wave generator is compared with it. The result is a pulse width modulation signal (PWM), and then the PWM signal Amplify and restore to analog audio signal. Therefore, the PWM power amplifier uses the pulse width to simulate the analog audio amplitude, and the information transmission process is analog, non-quantized, and non-coded. And because of the current performance limitations of the device, it is impossible for the PWM power amplifier to use a sampling frequency that is too high, and the performance index has not yet reached the Hi-Fi level. The digital power amplifier uses some pulses with a fixed width to digitally quantize and encode the analog audio signal, making the audio signal more realistic.
Second, the difference between digital power amplifier and analog power amplifier
Digital power amplifiers have completely different working methods from traditional analog power amplifiers, so they overcome some of the inherent shortcomings of analog power amplifiers and have some unique characteristics.
1. Overload capability and power reserve
The overload capacity of digital power amplifier circuits is much higher than that of analog power amplifiers. The analog power amplifier circuit is divided into Class A, Class B or Class AB power amplifier circuits. During normal operation, the power amplifier tube works in the linear region; when overloaded, the power amplifier tube works in the saturation region, harmonic distortion occurs, and the degree of distortion increases exponentially. The sound quality quickly deteriorates. The digital amplifier is always in the saturation zone and cut-off zone when the power is amplified. As long as the power amplifier tube is not damaged, the distortion will not increase rapidly, as shown in Figure 1. 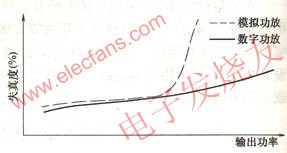
Figure 1 Comparison of overload distortion between all digital power amplifier and ordinary power amplifier
Because the digital power amplifier uses a switching amplifier circuit, the efficiency is extremely high, up to 75% "90% (the analog power amplifier efficiency is only 30%" 50%), and it basically does not generate heat when working. Therefore, it does not have the static current consumption of the analog power amplifier. Almost all of the energy is reserved for audio output. There is no analog amplification and no negative feedback before and after it is added, so it has better "power" characteristics and good transient response. "Sense" is very strong.
2. Crossover distortion and mismatch distortion
Analog class B power amplifier zero-crossing distortion, which is caused by the nonlinear characteristics of the transistor at low current and caused by the distortion at the positive and negative crossings of the output waveform (the transistor will work in the cut-off region when there is a small signal, no current passes, resulting in output Severely distorted). The digital power amplifier only works in the switching state, and will not produce crossover distortion.
Analog power amplifiers have inconsistent push-pull tube characteristics that cause asymmetrical mismatch distortion in the output waveform. Therefore, when designing a push-pull amplifier circuit, the requirements for the power amplifier tube are very strict. The digital power amplifier has no special requirements for the matching of the switch tubes, and basically can be used without strict selection.
3. Matching of amplifier and speaker
Because the internal resistance of the power amplifier tube in the analog power amplifier is large, when matching speakers of different resistances, the working state of the analog power amplifier circuit will be affected by the size of the load (speaker). The internal resistance of the digital power amplifier does not exceed 0.2Ω (the internal resistance of the switch tube plus the internal resistance of the filter), and the resistance value (4 "8Ω) relative to the load (speaker) is completely negligible, so there is no matching problem with the speaker.
4. Transient intermodulation distortion
Almost all analog power amplifiers use a negative feedback circuit to ensure their electro-acoustic index. In the negative feedback circuit, in order to suppress parasitic oscillations, a phase compensation circuit is used, which will cause transient intermodulation distortion. The digital power amplifier does not use any analog amplifier feedback circuit for power conversion, thus avoiding transient intermodulation distortion.
5. Sound image localization
For analog power amplifiers, there is generally a phase difference between the output signal and the input signal, and when the output power is different, the phase distortion is also different. The digital power amplifier uses digital signal amplification to make the output signal and input signal phase exactly the same, and the phase shift is zero, so the sound image positioning is accurate.
6. Upgrading
The digital power amplifier can obtain high power by simply replacing the switching amplifier module. High-power switch amplifying modules have low cost and broad development prospects in professional fields.
7. Production debugging
The simulation power amplifier has debugging problems at all levels of work points, which is not conducive to mass production. The digital power amplification part is a digital circuit, which can work normally without debugging, and is particularly suitable for large-scale production.
Third, the difference between digital power amplifier and "digital" power amplifier, "digital" power amplifier
The so-called "digital" amplifier only adopts the method of digital signal processing on the pre-stage. After the analog audio signal or digital audio signal is input, the existing digital audio processing integrated circuit is used to implement some such as sound field processing, digital delay Reverberation and other functions, and finally through the analog power amplifier module for audio amplification. Its typical circuit block diagram is shown as in Fig. 2. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the interfaces of each module are in analog mode. The schematic block diagram of the digital sound field processing module is shown in Figure 3. 
Figure 2 Block diagram of the digital power amplifier circuit Figure 3 Block diagram of the digital sound field processing module
Although various integrated circuit manufacturers have launched digital sound field processing, digital karaoke and digital Dolby decoding integrated circuits. However, since the current power amplifier can only receive analog audio signals, the interfaces of various integrated circuits are also mostly analog. This requires repeated analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion, which introduces quantization noise and deteriorates the sound quality.
In addition to the interface for the speaker (this is because the speaker can only accept analog audio signals), the audio signal is processed in the form of a digital signal (including power amplification); for analog audio signals, it must be It can be processed only after being converted into a digital signal.
The introduction of digital power amplifiers in an era where digital audio is already available may have a significant impact on the development of audio technology.
The difference between digital power amplifier, class D power amplifier and analog power amplifier
1. The difference between digital power amplifier and class D power amplifier