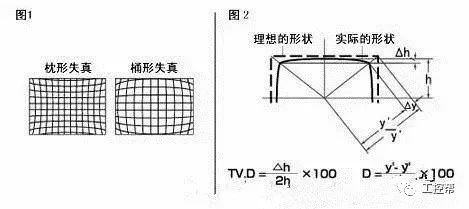
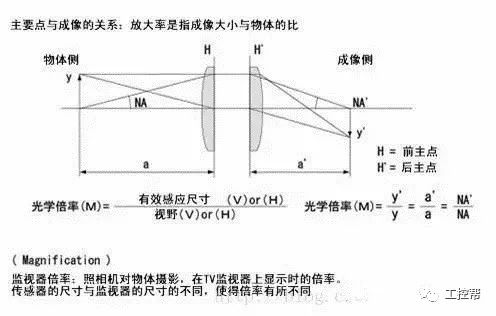
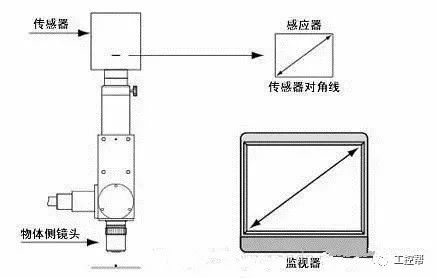
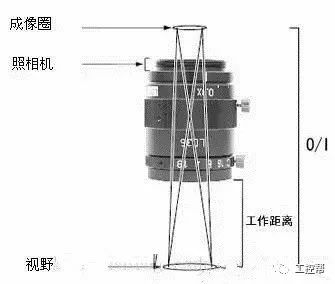
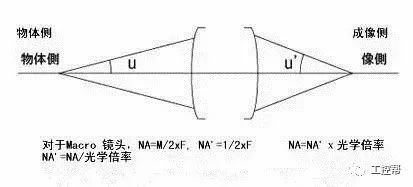
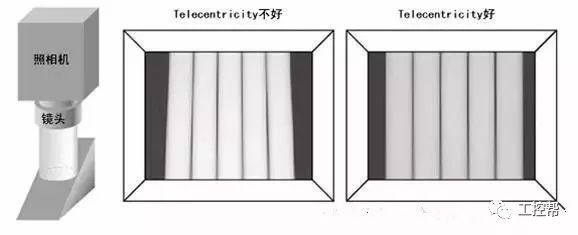
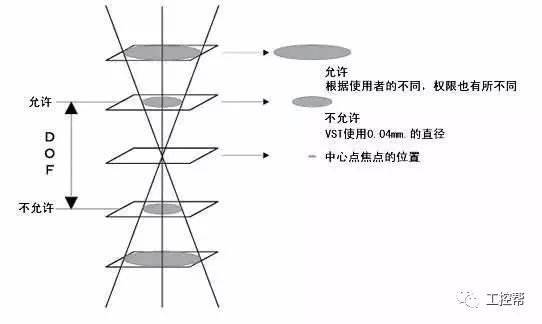
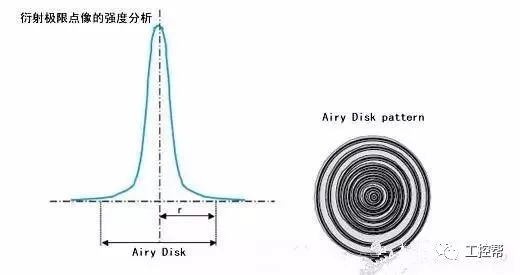
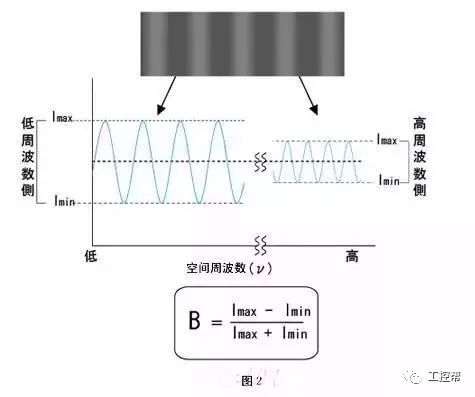
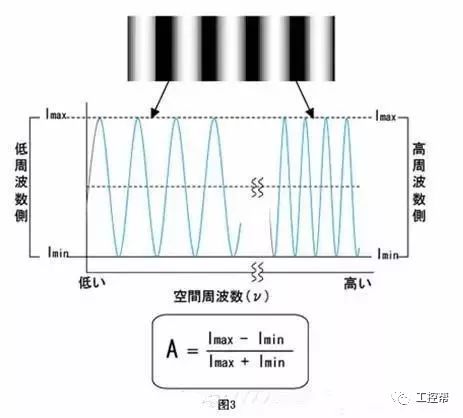
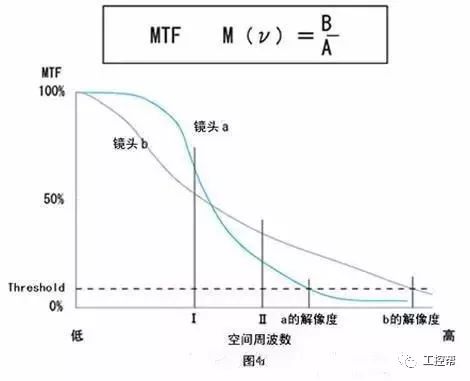
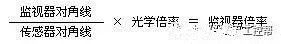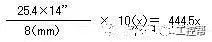In a machine vision system, the lens is equivalent to a human eye, and its main function is to focus the optical image of the target on the photosensitive surface array of the image sensor (camera). All image information processed by the vision system is obtained through the lens, and the quality of the lens directly affects the overall performance of the vision system. The following is a detailed explanation of the technical terms related to machine vision industrial lenses. Can be divided into pincushion distortion and barrel distortion, as shown below: The calculated value of the actual side length of the warped shape and the percentage of the ideal shape. Calculation method: Example: VS-MS1+10x lens 1/2†CCD camera, imaging on a 14†monitor The 0.1mm object obtained on the monitor is 44.45mm imaging. ※Depending on the scanning status of the TV monitor, there may be some changes in the above simple calculations. It shows that the interval of 2 points can be seen 0.61x using wavelength (λ) / NA = resolution (μ) The above calculation method can theoretically calculate the resolution, but does not include distortion. ※Use wavelength is 550nm The number of black and white lines can be seen in the middle of 1mm. Unit (lp)/mm. The number of spatial cycles and contrast used to reproduce the change in the shading of the surface of the object during imaging. The distance from the lens barrel to the object The distance between objects is the length from object to image. The imaging size φ is to be input to the camera sensor size. C-mount: 1" diameter x 32 TPI: FB: 17.526mm CS-mount: 1" diameter x 32 TPI: FB: 12.526mm F-mount: FB: 46.5mm M72-Mount: FB manufacturers are different Field of view refers to the range of the object side seen after using the camera Longitudinal length (V) / optical magnification (M) of the effective area of ​​the camera = field of view (V) Horizontal length (H) / optical magnification (M) of the effective area of ​​the camera = field of view (H) * The field of view on the technical data refers to the value calculated from the general values ​​of the light source and the effective area. The longitudinal length (V) or (H) of the effective area of ​​the camera = the size of one pixel of the camera × the effective number of pixels (V) or (H) is calculated. Depth of field refers to the distance of an object after imaging. Also, the range on the camera side is called the depth of focus. The value of the specific depth of field is slightly different. f (Focal Length) The distance from the rear principal point (H2) of the optical system to the focal plane. When the lens is from infinity, the value represented by the brightness is smaller and brighter. FNO = focal length / incident aperture or effective aperture = f / D The brightness of the lens at a limited distance. Effective F = (1 + optical magnification) x F# Effective F = optical magnification / 2NA NA on the object side = sin uxn NA' = sin u'x n' on the imaging side As shown in the figure below, the angle u, the refractive index of the object side, and the refractive index of the imaging side 'n' NA = NA' x magnification The contrast is the percentage of the central illuminance to the surrounding illuminance. A lens in which the chief ray is parallel to the lens source. There are telecentricity on the object side, telecentricity on the imaging side, and telecentric lines on both sides. Telecentricity refers to the magnification error of an object. The smaller the magnification error, the higher the Telecentricity. Telecentricity has a variety of uses, and it's important to grasp Telecentricity before the lens is used. The chief ray of the telecentric lens is parallel to the optical axis of the lens. Telecentricity is not good, and the use of telecentric lenses is not good; Telecentricity can be easily confirmed using the following figure. Depth of Field can be calculated using the following formula: Depth of field = 2 x Permissible COC x Effective F / Optical magnification 2 = Permissible error value / (NA x optical magnification) (Using 0.04mm Permissible COC) Airy Disk refers to a concentric circle that is actually formed when the light is concentrated by a lens without distortion. This concentric circle is called Airy Disk. The radius r of the Airy Disk can be calculated by the following formula. This value is called resolution. r = 0.61λ/NA The radius of the Airy Disk changes with the wavelength. The longer the wavelength, the harder it is to concentrate on one point. Example: The lens wavelength of NA0.07 is 550nm r=0.61*0.55/0.07=4.8μ MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) refers to the change in the shade of the surface of the object, and the image side is also reproduced. Indicates the imaging performance of the lens and the degree to which the contrast of the image is reproduced. Test contrast performance using a black and white interval test with a specific spatial cycle number. The spatial cycle number refers to the degree to which the distance of 1 mm changes. As shown in Fig. 1, the black and white matrix wave has a contrast ratio of 100% in black and white. After the object is photographed by the lens, the contrast of the image is quantified. Basically, no matter what lens, there will be a decrease in contrast. The final contrast is reduced to 0%. , can not make the difference in color. Figures 2 and 3 show the change in the number of spatial cycles of the object side and the imaging side. The horizontal axis represents the number of spatial cycles, and the vertical axis represents the brightness. The contrast between the object side and the image side is calculated by A and B. The MTF is calculated from the ratio of A and B. The relationship between resolution and MTF: Resolution is the interval between how two points are separated. Generally, the value of the resolution can be used to determine whether the lens is good or bad, but the actual MTF has a great relationship with the resolution. Figure 4 shows the MTF curves for two different lenses. Lens a has low resolution but high contrast. Lens b has low contrast but high resolution.
tweeter speaker is designed to reproduce high audio frequencies, typically from around 2,000 to 20,000 Hz (2KHz to 20KHz).
Traditional speakers produce sound by using an electromagnet to move a flexible cone back and forth. They use drivers to help translate electrical signals into physical vibrations so that you can hear recorded sounds. Tweeters are one of the three main speaker types.
Any recording is a very complex combination of different tones, frequencies, and other characteristics. Music is made by different instruments, the voice of singers, and items added when music is recorded. Without tweeters, you will be neglecting a crisp and well-detailed sound to your ears. I`m pretty sure you want a better experience, not a bad one.
Our company's tweeter speaker products not only have high quality and competitive prices, is a Chinese supplier trusted by buyers all over the world market, choose us and you have chosen a bright and brilliant future
"Tweeter Speaker ,Tweeter Driver ,Kicker Tweeters,Tweeter Audax" NINGBO LOUD&CLEAR ELECTRONICS CO.,LIMITED , https://www.loudclearaudio.com