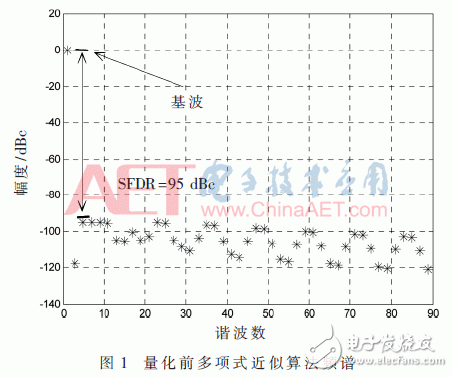
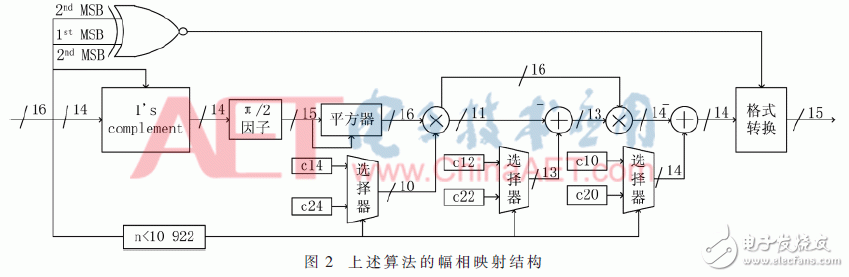
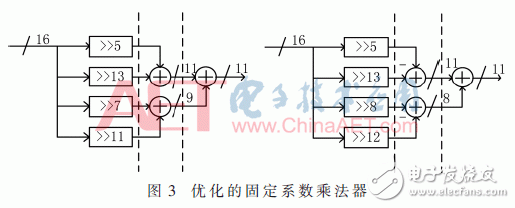
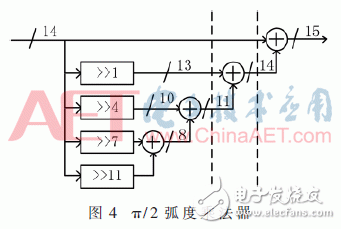
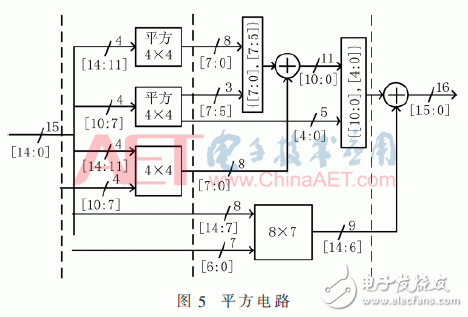
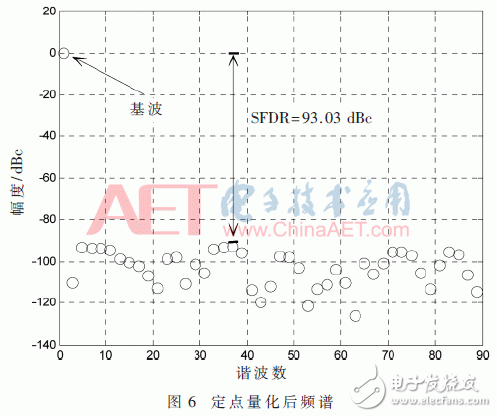
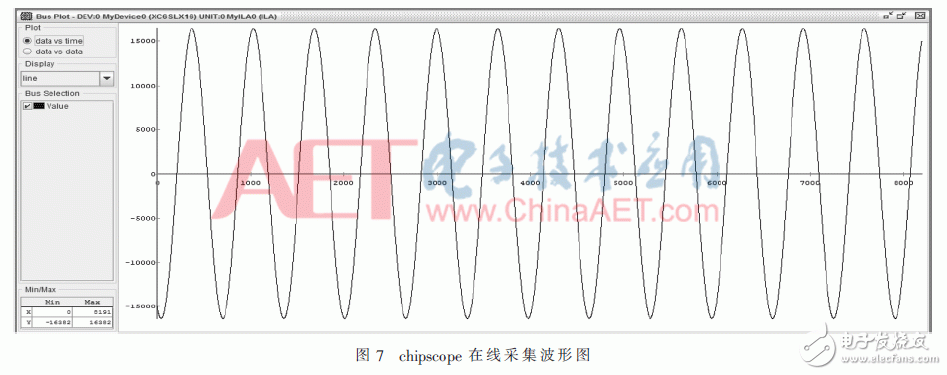
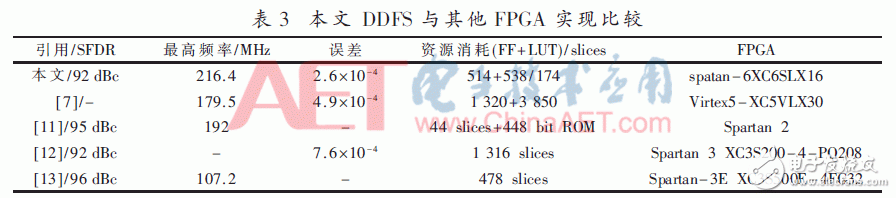
The induction magnetometer is based on the Faraday electromagnetic induction principle and is used to detect low-frequency alternating magnetic fields in near-Earth space. It usually comes with a standard signal source for on-orbit calibration. The high-quality calibration detection signal is the prerequisite to ensure the scientific information of the changing magnetic field waveform and frequency spectrum detected by the induction magnetometer. Direct Digital Frequency Synthesis (DDFS) was first proposed by J. TIerney in 1971. DDFS uses digital technology to synthesize frequencies with phase as the starting point. It has high stability, high resolution and small phase noise. DDFS's performance indicators far exceed traditional frequency synthesis technology, so it is widely used in digital communications and precision instruments . Using direct digital frequency synthesis technology can provide a high-precision standard calibration signal source for the induction magnetometer. The frequency of the DDFS output signal is expressed as: Among them, FCW is the frequency control word, and the phase-amplitude mapping structure of the traditional method is based on the look-up table ROM. The ROM capacity increases exponentially with the output bit width D. In order to reduce the ROM capacity, the bit width of the phase accumulator is truncated and the high W bit is reserved as the input bit width of the phase amplitude mapping. Due to the phase truncation, the Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) of the synthesized signal will be significantly reduced. The non-quantized output SFDR is a linear function of the truncated word length, which can be approximated as: D is the bit width of the output signal, and the SFDR should be greater than the quantized signal-to-noise ratio. The quadrant compression method using the quadrant symmetry of the trigonometric function can further reduce the capacity of the lookup table and save 75% of resource usage. Relying only on the truncation and quadrant compression of the phase word cannot significantly reduce the capacity of the look-up table. A variety of other amplitude-phase mapping methods have been extensively studied, and they are usually divided into two categories: The angle decomposition method of ROM compression algorithm and the amplitude-phase conversion technology of ROM-Less. The ROM-Less type DDFS gets rid of the limitation of the large-capacity look-up table, and uses logic operations to convert the phase into an amplitude. Such as rotation angle algorithm (CORDIC algorithm), Taylor series expansion algorithm, piecewise linear interpolation and piecewise polynomial approximation. In the piecewise polynomial approximation method, with the increase of the order and the number of pieces of the piecewise polynomial approximation algorithm, a smaller amplitude error and high SFDR are obtained while increasing hardware resource occupation and power consumption. Therefore, balancing the number of segments and the highest order of the piecewise polynomial approximation algorithm is the key to the algorithm hardware to balance performance and resource occupation. The objective function is approximated by two unequally divided four-order even power polynomials, and the first quarter period of the cosine function is fitted based on the interval compression method. The phase segment point α divides [0, π/2] into two segments, and the fitting objective function expression is: pij (i=1, 2, j=0, 2, 4) is expressed as the i-th segment, j-th order coefficient. The maximum amplitude error MAE and SFDR are two important indicators for evaluating the output signal of DDFS. When the MAE is reduced to 0, the theoretical SFDR is infinite. Due to the limitation of quantization bit width and hardware resources, it cannot be realized in actual hardware circuit. SFDR can be increased by reducing MAE. When the value of α is fixed, the polynomial coefficient corresponding to the minimum error of the objective function is obtained through the minimum mean square MMSE: At the phase point α=π/3, the maximum MMSE is obtained, and the maximum absolute error is 2.1&TImes;10-4<2-12. Table 1 shows the coefficients of the fitting result polynomial. The theoretical upper limit of SFDR of f(x) can be obtained by Fourier series expansion. Since the synthesized cosine signal is even symmetrical and has quarter-quadrant symmetry, only odd cosine harmonic coefficients are non-zero . Figure 1 shows the Fourier transform spectrum of the formula (4) algorithm. The theoretical upper limit of the SFDR shown in the figure is 94.98 dBc. The theoretical upper limit of SFDR output based on a single-segment fourth-order even power polynomial phase-amplitude mapping output is 74.352 dBc. The SFDR of the output signal of the above approximation algorithm is greater than the upper limit by more than 20 dBc. Using Horner's law to implement even-order polynomials of 4th order can reduce the use of a multiplier and reduce the computational complexity. The DDFS structure designed in this article theoretically has a maximum SFDR of 94.98 dBc. According to formula (2), the addressing bit width W should have W "94.98, taking W = 16, and according to formula (3), the output D is 15 bits. The above DDFS structure diagram is shown in Figure 2. 2.1 Fixed coefficient multiplier optimization The digital circuit can simplify the operation of the integer power of 2 to logical left or right shift, In the formula, hik ∈ {-1, +1}, dik ∈ {..., -2, -1, 0, +1, +2,...}. The maximum value of M is restricted by the word length of the multiplicand and should be as small as possible to reduce the complexity of the structure. Figure 3 shows the optimization of a multiplier with a quantization bit width of 14, where the dotted line represents the pipeline stage. The fixed coefficient multiplier required to generate π/2 radians is shown in Figure 4. 2.2 Square circuit optimization The squaring operation is optimized and decomposed into parallel truncation operation, instead of simple interception after operation, and reduces the complexity of the circuit. The input of the squaring circuit required in Figure 2 is 15 bits and the output is 16 bits. The square circuit of the improved 4-stage pipeline is shown on the right in Figure 5. Compared with direct truncation, there is only 1 LSB rounding error, which is less than 2-15. The influence of quantization error on SFDR is nonlinear. The Nelder-Mead nonlinear simplex method is used to recalculate the parameters in equation (12). The optimized coefficients are shown in Table 2. Figure 6 shows the frequency spectrum of the output signal after fixed-point quantization. The SFDR is about 93.03 dbc, which is about 2 dBc away from the maximum theoretical SFDR calculated by floating-point numbers. Therefore, the design method in this article can improve the SFDR of the synthesized signal without significantly increasing the consumption of hardware resources. In order to verify the effectiveness of the structure DDFS designed by the above algorithm, the ISE is used as the development platform and the system simulation verification is performed based on the Xillinx spatan-6 series XC6SLX16 FPGA. Fig. 7 is the waveform data collected online using the virtual logic analyzer chipscope when the program is downloaded to the FPGA when FCW=127. Table 3 shows the comparison between the design method in this article and other FPGA-based DDFS implementations. Compared with the algorithm in literature [7], the method in this paper can obtain an output signal with smaller output error and greater operation frequency under the condition of using fewer hardware resources. Compared with literature [11] ~ literature [13], under the same SFDR level, the hardware resources used in this paper are reduced, and the maximum computing frequency is not affected. In this paper, the two unequal-divided fourth-order even power polynomials obtained by the least-average method are used as the cosine function fitted by the objective function, which can produce a spurious-free dynamic range greater than about 20 dBc in the single-segment case. According to the upper bound of the obtained SFDR, the optimal phase-amplitude mapping input and output bit widths are analyzed and selected. The fixed coefficient multiplier and squarer are optimized, and the errors caused by quantization, rounding and truncation are reduced through the Nelder-Mead nonlinear simplex method. The difference between the theoretical limit and the theoretical limit is only 2 dBc. At the same time, the DDFS structure can reduce the use of resources compared with other design methods under the same SFDR level. The standard signal source provides a new design idea. Pvc Wire,Aluminium Core Wire,Aluminium Core Pvc Insulation Wire,Aluminium Conductor Grounding Wire Baosheng Science&Technology Innovation Co.,Ltd , https://www.bscables.com
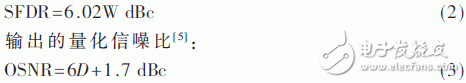
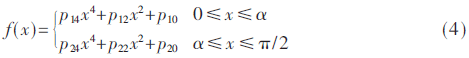
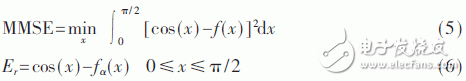

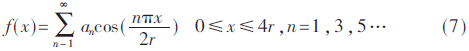





DDFS Research on Piecewise Polynomial Approximation and Analysis of the Design Process of FPGA Implementation
0 Preface