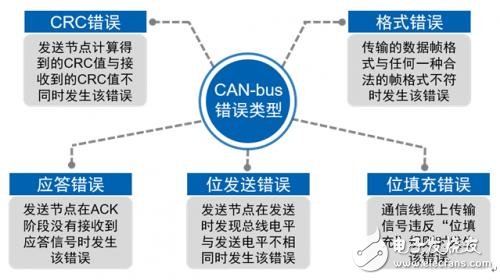
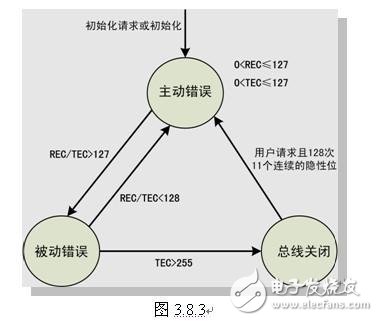
CAN is the abbreviation of Controller Area Network (CAN). It was developed by German BOSCH company, which is famous for developing and producing automotive electronics products, and eventually became an international standard (ISO11898). It is one of the most widely used fieldbuses in the world. At the beginning of the establishment, the CAN bus is positioned in the field bus inside the car, which has the advantages of fast transmission speed, high reliability and flexibility. In the 1990s, CAN bus began to be gradually promoted in the automotive electronics industry. It has become the communication protocol of choice in the automotive electronics industry, and has been widely used in medical equipment, industrial production, building facilities, transportation and other fields. The CAN bus protocol defines five error types for monitoring data transmission on the bus. These five errors include: 1. Bit Error: Nodes on the CAN bus also detect the level on the bus while transmitting data. If the data sent outside the arbitration domain is inconsistent with the data monitored by the node, the CAN bus generates a bit error. However, if the node detects that the level on the bus does not match the transmitted value when transmitting the ACK segment or the passive error flag, it does not determine that a bit error has occurred. 2. Stuff Error: In the CAN bus transmission, as long as five identical bits appear consecutively in the detection start, arbitration field, control field, data field and CRC check part of the message, an additional bit needs to be inserted, which is filled by the CAN bus bit. mechanism. In CAN bus communication, if a node detects six consecutive identical levels, it determines that a bit stuffing error has occurred on the bus. 3. CRC check (CRCError): The data frame of the CAN bus comes with a CRC check. The CRC of this frame is also calculated while the data is being transmitted, and the check code is sent at the end of the data frame. After receiving the data frame, the receiving node calculates a CRC code of the data field in the received data frame, and compares with the received CRC check code to determine whether the received data is accurate. If not, a CRC check occurs. error. 4. Form Error: An illegal bit appears in the fixed format bit field. For example, if a dominant level occurs in the CRC delimiter that is supposed to be a recessive bit, the monitoring node determines that a format error has occurred. 5. Acknowledgement Error: In the CAN bus transmission, the response field sent by the transmitting node is a recessive bit, and the receiving node needs to send a dominant bit coverage recessive bit to the bus in the response field to indicate that the acceptance is completed. If the transmitting node detects that the response field of the frame is still a recessive bit, it indicates that a response error has occurred, and no node receives the data and the transmission fails. When the node detects an error, it sends an error frame to the bus while the local error counter is incremented. Each node on the CAN bus has two error registers: a receive error counter and a transmit error counter, which are used to count receive and transmit errors, respectively. An error is detected and the corresponding error counter is incremented; a successful message is sent or received, and the corresponding error counter is decremented until it is zero. When the error counter is less than 127, the node is in the active error state. When the error counter is 127 to 255, the node is in the passive error state. When the error counter exceeds 255, the node enters the offline state, and the node in the offline state will no longer participate in the bus. data transmission. A station that detects an error condition indicates an error by sending an error flag. For the wrong active node, the error message is the active error flag; for the passive node, the error message is the passive error flag. If the station detects an error, whether it is a bit error, a padding error, a situation error, or a response error, the station will send an error flag message at the next bit. When a CRC error is detected, the transmission of the error flag begins with the bit following the ACK delimiter, unless other error flags have begun to be sent. Desktop Phone Holder,Desktop Mobile Phone Holder,Adjustable Desktop Phone Holder,Universal Desktop Cell Phone Holder Ningbo Luke Automotive Supplies Ltd. , https://www.car-phone-holder.com