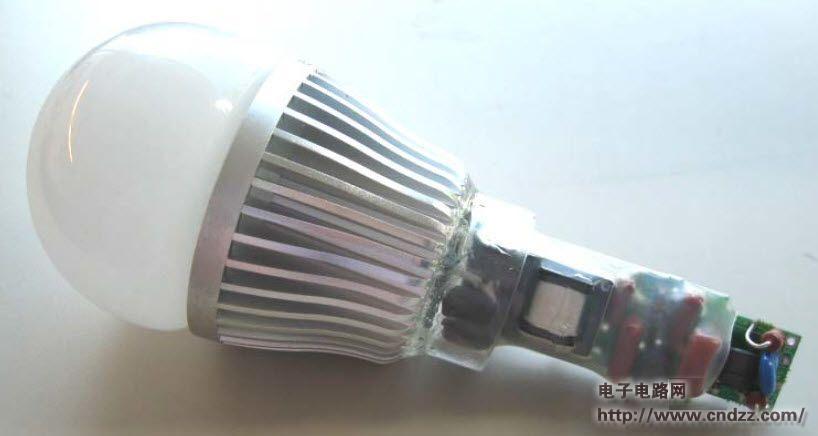
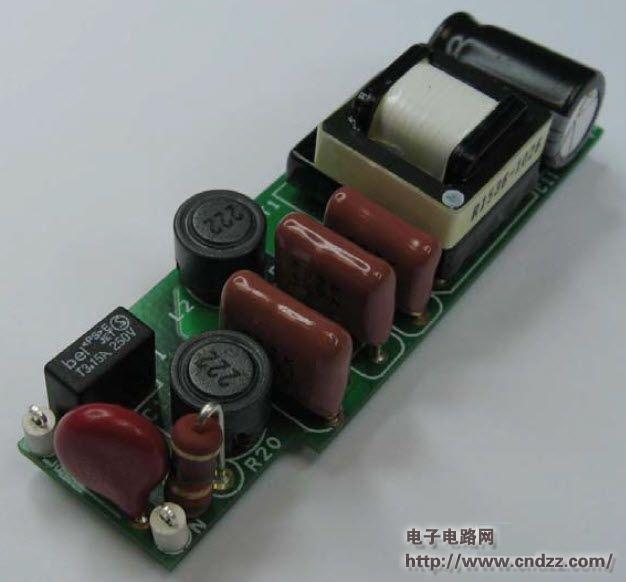
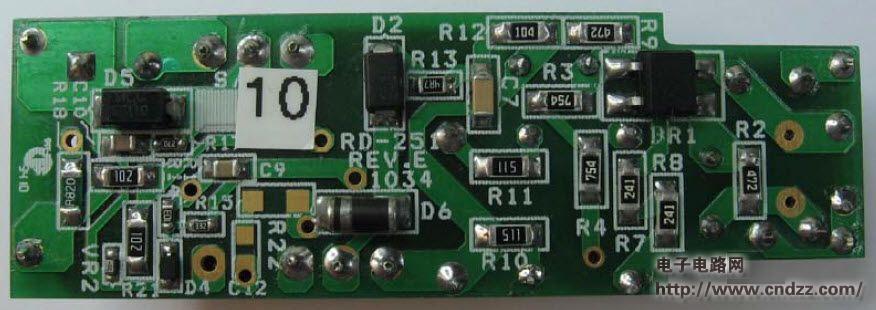
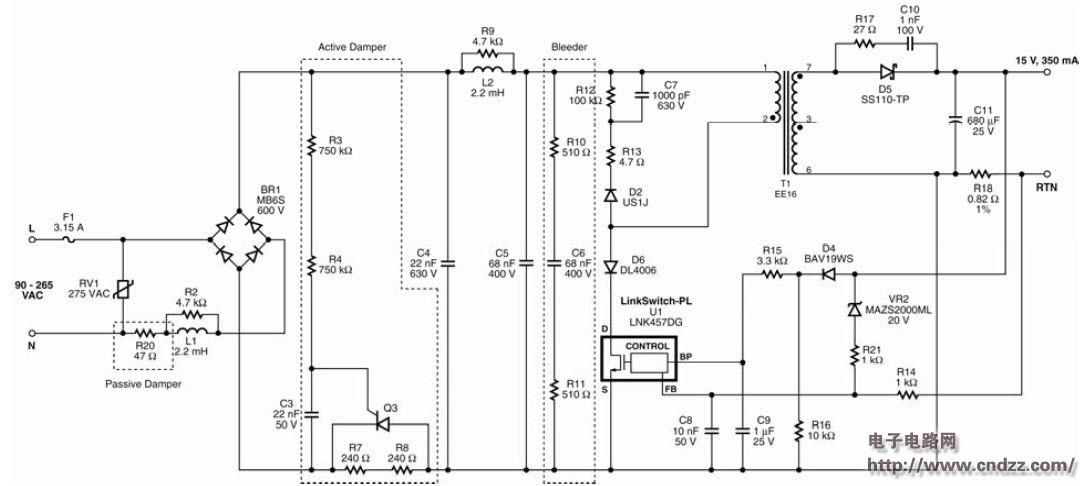
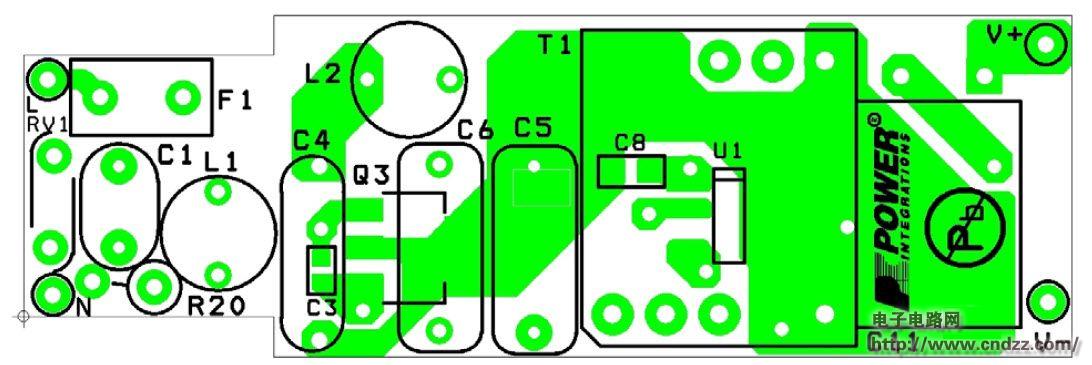
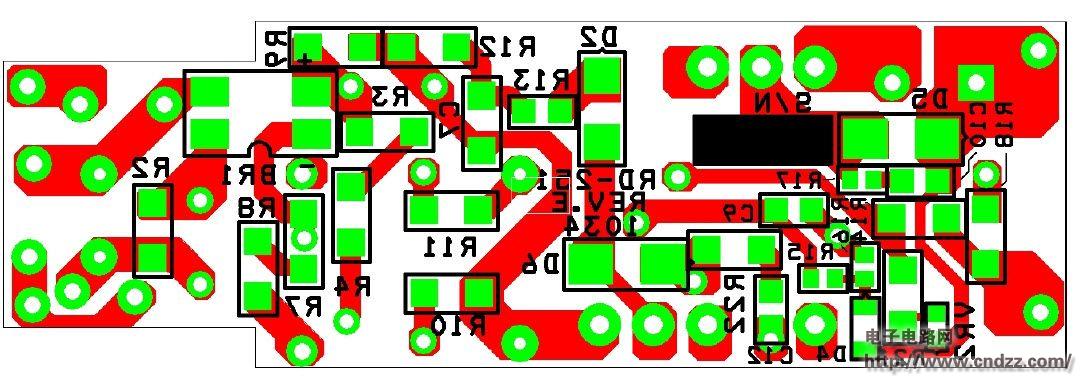
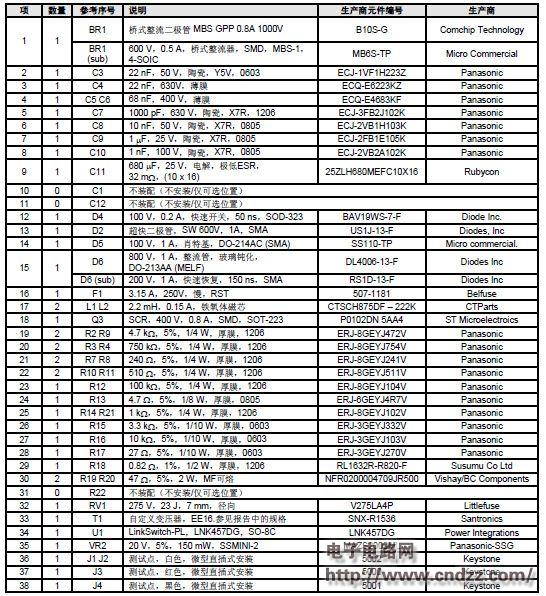
Summary: This document is an engineering report describing a non-isolated LED driver (power supply) designed using the LinkSwitch-PL family of devices, the LNK457DG. The RD-251 provides a single 350 mA constant current output at 12V and 18V LED string voltages. Using a standard AC mains thyristor dimmer reduces the output current to 1% (3 mA), which does not cause LED load performance to be unstable or flicker. The circuit is compatible with both low cost leading edge dimmers and more complex trailing edge dimmers. This circuit is designed to operate over a universal AC input voltage range (85 VAC to 265 VAC, 47 Hz to 63 Hz), but will not cause damage over an input voltage range of 0 VAC to 300 VAC. This improves field application reliability and extends the life of online voltage dips and surges. The LinkSwitch-PL-based design provides a high power factor (>0.9) to help meet the requirements of all current international standards, making a single design universal. The power supply is designed to meet the requirements of a standard pear-shaped (A19) LED replacement lamp. The output is non-isolated and requires a mechanical design of the housing to isolate the power output and LED load from the user. This document includes power specifications, circuit diagrams, bill of materials, transformer documentation, printed circuit board layout, and performance data. 5W dimmable non-isolated LED driver PCB physical map 5W dimmable non-isolated LED driver circuit diagram 5W dimmable non-isolated LED driver PCB top layout 5W dimmable non-isolated LED driver PCB bottom layout 5W dimmable non-isolated LED driver component list See the PDF document for details (click to download) Polycrystalline sillicon (also called: polysilicon, poly crystal, poly-Si or also: multi-Si, mc-Si) are manufactured from cast square ingots, produced by cooling and solidifying molten silicon. The liquid silicon is poured into blocks which are cut into thin plates. The solidification of the material results into cells that contain many crystals, making the surface of the poly-Si/ mc-Si cell less perfect than its mono-Si counterpart. Due to these defects, polycrystalline cells absorb less solar energy, produce consequently less electricity and are thus less efficient than monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si) cells. Due to their slightly lower efficiency, poly-Si/ mc-Si cells are conventionally a bit larger, resulting in comparably larger PV modules, too. This factor has to be considered if space is limited. Nevertheless, the advantage of poly-Si/ mc-Si cells is that they are easier and thus cheaper to produce. Poly Solar Cell,Solar Photovoltaic Cell,Most Efficient Solar Cell,Polycrystalline Solar Cells Wuxi Sunket New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.sunketsolar.com