EMC measurement equipment selection
In the EMC test equipment selection, often encountered such problems: EMI receiver and spectrum analyzer in the end what is the difference, why use EMI test receiver? Based on CISPR16-1 (GB/T6113) and GJB152, this article analyzes the test principle of the receiver and analyzes the choice of receiver and spectrum test equipment to provide reference. The receiver that meets the standard is the only choice for EMC conformity test.
1. The principle difference between receiver and spectrum analyzerThe spectrum analyzer is the main tool for the current spectrum analysis. In particular, the swept frequency heterodyne spectrum analyzer is the mainstream of the spectrum analyzer. The frequency sweep technique is used to obtain the heterodyne signal through the frequency sweep signal source for dynamic analysis in the frequency domain.
The receiver is the main tool for EMC testing. Based on the point frequency method, the principle of local oscillator tuning is used to test the level value of the corresponding frequency point. The scanning mode of the receiver should be obtained by step-point frequency tuning.
According to the principle of operation, spectrum analyzers and receivers can be divided into analog and digital categories. Heterodyne analysis is currently the most widely used method of reception and analysis. The following is an analysis of the main differences between a heterodyne analyzer and a receiver.
From the schematic diagram, the spectrum analyzer is similar to the receiver, but the spectrum analyzer and the receiver are quite different in the following aspects: front-end preselector; local oscillator signal scanning; IF filter; spurious signal and accuracy.
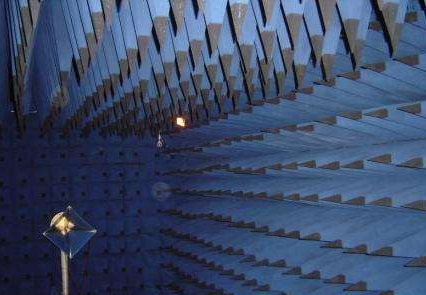
Front-end processing of input RF signals
The receiver and the spectrum analyzer process the signals on the input side differently.
The signal input of the spectrum analyzer usually has a set of simpler low-pass filters, and the receiver should use a preselector with strong immunity to wide-band signals. A set of fixed bandpass filters and a set of tracking filters are usually included to complete the preselection of the signal.
Due to the effects of harmonics, crosstalk, and other spurious signals of the RF signal, spectrum analyzer and receiver test errors are caused. Compared with spectrum analyzers, receivers require higher accuracy, which requires a preselector at the front end of the receiver to be more selective than conventional spectrum analyzers.
Receiver selectivity is clearly defined in GB/T6113 (CISPR16).
Local oscillator signal adjustment
With current EMC measurements, people need not only to manually tune search frequency points, but also to quickly and intuitively observe the EUT's frequency level characteristics. This means that the local oscillator signal can be tested both at the specified frequency point and at a certain frequency range.
The spectrum analyzer implements frequency sweep measurements by sweeping the signal source. The sweep signal source is usually controlled by a ramp or sawtooth signal and scanned within a preset frequency span to obtain the desired mixed frequency output signal.
The frequency sweep of the receiver is stepped, discrete, discrete point frequency testing. The receiver performs the level measurement at each frequency point according to the operator's preset frequency interval, and the measured test result curve is actually the result of a single point frequency test.
IF filter
The bandwidth of the IF filter of the spectrum analyzer and the receiver is different.
It is usually defined that the resolution bandwidth of the spectrum analyzer is a 3 dB bandwidth of the amplitude-frequency characteristic, and the IF bandwidth of the receiver is a 6 dB bandwidth of the amplitude-frequency characteristic. When the spectrum analyzer and the receiver set the same level of bandwidth, their actual test values ​​for the signals are different. Specific performance as shown below:
Spectrum Analyzer RBW Filter Receiver IFBW Filter
It can be seen from the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the spectrum analyzer and the receiver IF filter that when the 3 dB bandwidth B3 of the spectrum analyzer is set to the same value as the receiver 6 dB bandwidth B6, the amplitude and frequency characteristics of the signals actually passed through the two filters are different. . According to the EMC standard, the bandwidth should be 6dB for civilian or military standards.
Detector
According to EMC standards, test receivers are required to have peak, quasi-peak, and average detectors. Universal spectrum analyzers typically have peak and average detectors, no quasi-peak detectors, and EMC standard limits typically include quasi-peak values. Limit value.
Accuracy
From the receiver's signal processing and EMC testing requirements, the receiver has higher accuracy and lower spurious response than the spectrum analyzer.
2 Difference between receiver and spectrum analyzer in EMC test applicationIn the current market, we can see some receivers that have been transformed by spectrum analyzers. If they are used for testing, they must meet the corresponding standards. For civil EMC testing, the measurement equipment standard is based on CISPR16-1 (GB/T6113). For military standard testing, the standard basis for measuring equipment is GJB152 (MIL-STD462).
Based on the principle analysis of the previous chapter, we can summarize the following simple formula:
Universal Spectrum Analyzer + Preselector +6dB IF Filter, Three Detectors + Point Frequency Test Function + High Precision Signal Processing = Receiver
The items on the left of the formula are not simply listed. Each item has special requirements. At the same time, according to the design principle, it must be operated according to the instrument manufacturer's instructions in order to achieve the corresponding requirements.
Preselector
The band selection must be based on the manufacturer's instructions. If the scan span setting is not appropriate, the fixed filter and follower filter in the preselector will not work properly.
Point frequency test and detector
When testing according to EMC standards, there are many cases where real-time testing of certain fixed frequency points is required. For example, many test engineers perform radiation interference tests, according to the standard requirements, need to select a suitable frequency point, rotate the turntable and the antenna, and quickly observe and record the level value of the point in real time. In this case, a receiver with a point frequency test function can be easily and accurately completed, and the universal spectrum analyzer cannot accurately measure the level change of a single frequency point in real time, and the spectrum analyzer for EMI test must have an increased function. When the scan span (SPAN) is zero, the test is performed quickly and accurately, not only the peak display, but also the quasi-peak and average values.
According to the standard CISPR16-1, when the peak, quasi-peak and average detectors are tested for impulse response, the receiver can perform point frequency monitoring on a single frequency to determine whether it meets the standard, and it is difficult for the universal spectrum analyzer to complete this measurement. of. Impulse response measurement is an important indicator to judge whether the receiver is suitable or not. Non-conformity can only be used as pre-test equipment.
3 ConclusionAccording to the principle analysis of the spectrum analyzer and receiver in this paper, the receiver designed for EMC test is the only choice suitable for the determination and certification test. Many pre-tested instruments, such as the spectrum analyzer built-in 6dB IF bandwidth, quasi-peak and average detectors, or spectrum analyzers plus pre-selectors, can not fully meet the requirements of the receiver, can only be used for factory pre-test.
ZGAR Foggy Box 7000
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
Our products include disposable e-cigarettes, rechargeable e-cigarettes, rechargreable disposable vape pen, and various of flavors of cigarette cartridges. From 600puffs to 5000puffs, ZGAR bar Disposable offer high-tech R&D, E-cigarette improves battery capacity, We offer various of flavors and support customization. And printing designs can be customized. We have our own professional team and competitive quotations for any OEM or ODM works.
We supply OEM rechargeable disposable vape pen,OEM disposable electronic cigarette,ODM disposable vape pen,ODM disposable electronic cigarette,OEM/ODM vape pen e-cigarette,OEM/ODM atomizer device.

ZGAR FB7000 Vape,ZGAR Foggy Box 7000 disposable electronic cigarette, FB7000 vape pen atomizer , FB7000 E-cig,Foggy Box 7000 disposable electronic cigarette,ZGAR Foggy Box 7000 disposable vape,zgar foggy box
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.zgarette.com