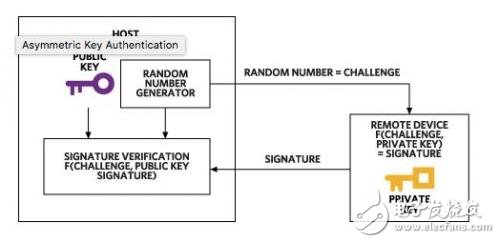
Currently, digital security is one of the hottest topics in the field of electronic design. For many engineers, when it comes to security, the first word that flashes in your mind may be encryption. There may be only a handful of people who think of security certification. Now that we understand the importance of security certification, let's discuss how to implement it. The easiest way to securely authenticate is to use a password. In the case of a smart meter, the device can send a password to the grid control system. The server verifies the password and then authorizes the next step. Although this method is very easy to understand, it is not the best method. It is easy for an attacker to listen to communications, record passwords, and then use it to securely authenticate non-real devices. Therefore, we believe that password-based security authentication methods are weak. Figure 1. Secure authentication based on symmetric encryption relies on a shared key between the host and the device. Secure authentication based on asymmetric encryption relies on two keys: a private key and a public key. Only the authenticated device knows the private key, and the public key can be disclosed to any party who wants to securely authenticate the device. As with the method discussed above, the host sends a challenge to the device. The device calculates the digital signature based on the challenge and private key and sends it to the host (Figure 2). But at this point, the host uses the public key to verify the digital signature. It is important that the function used to calculate the digital signature has specific mathematical properties. The most commonly used functions in asymmetric methods are RSA and ECDSA. Similarly, the device also submits a certificate that it knows the key, ie the private key, without revealing the key. Figure 2. Asymmetric key security authentication relies on public and private keys. 48V15Ah Lithium Ion Battery,48V15Ah Lithium Battery Pack,Li-Ion 48V15Ah Lithium Battery Pack,Echargeable Lithium Battery Pack 48V Jiangsu Zhitai New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zt-tek.com
However, security authentication is the basic function of a secure device or transaction. Let's take a family bank as an example. Obviously, you want confidential information such as balances and accounts to be encrypted. At this point, a small lock logo and "https://" will appear on your web browser. In other words, when the web browser establishes a secure connection, the first thing is to check the authenticity of the bank site; in other words, to secure the bank site. In fact, if the login and password information is sent to the phishing website, it is very harmful because these credentials can be further reused to perform unauthorized transactions in the name of the bank account holder, but the actual holder does not know. situation. Through the TLS/SSL protocol, secure Internet browsing is generally achieved, ensuring authenticity and confidentiality.
Security certification is also important for Internet of Things (IoT) applications: Untrusted endpoints can put the entire infrastructure at risk. Let's take the example of a smart meter connected to a power distribution system. An easy way for an attacker to break the grid is to load a virus or malware onto a smart meter. The disturbed meter then sends a fake message to the infrastructure, and the power consumption reflected is very different from the actual power consumption. The grid will be unbalanced; in worse cases, the attack may trigger a power outage across the network. To avoid this, you must verify the authenticity of the meter hardware and firmware. The process of securely authenticating firmware is called secure boot.
A better way to perform secure authentication in the digital domain is the challenge-response method. Let's look at two methods of challenge-response: one based on symmetric encryption and the other based on asymmetric encryption.
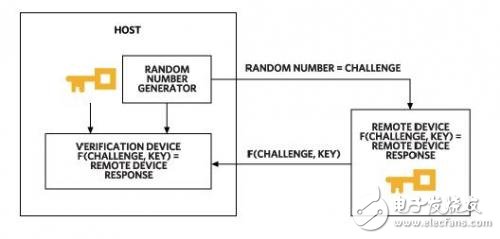
Symmetric encryption security authentication relies on shared keys. The host and the authenticated device hold the same key. The host sends a random number to the device, which is a challenge. The device calculates a digital signature that is a function of the key and challenge and is sent back to the host. The host performs the same operation and compares the results. If the two calculations are consistent, the device passes the security certification (Figure 1). In order to ensure that the results are not mimicked, it is necessary to use functions with sufficient mathematical properties; for example, it must be guaranteed that it is impossible to obtain a key from the calculation result. Security hash functions such as SHA-256 meet these requirements. For the challenge-response method, the device proves that it knows the key without revealing the key. Even if an attacker intercepts the communication, he or she cannot access the key.