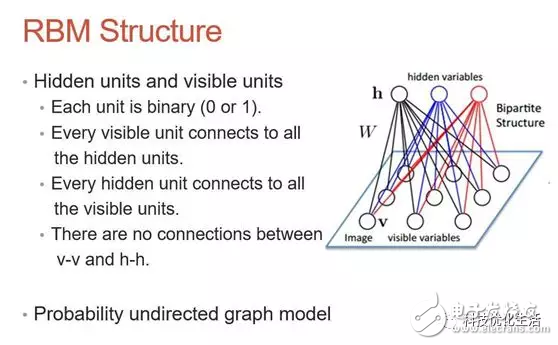
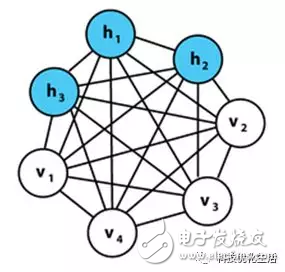
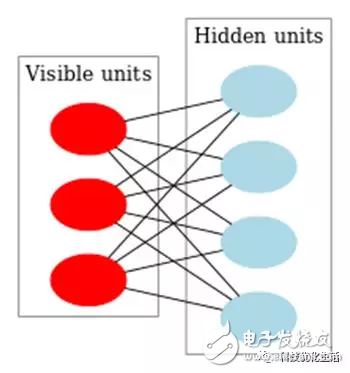
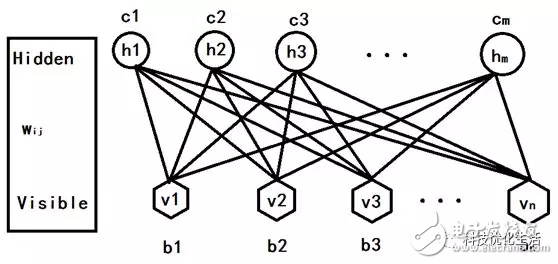
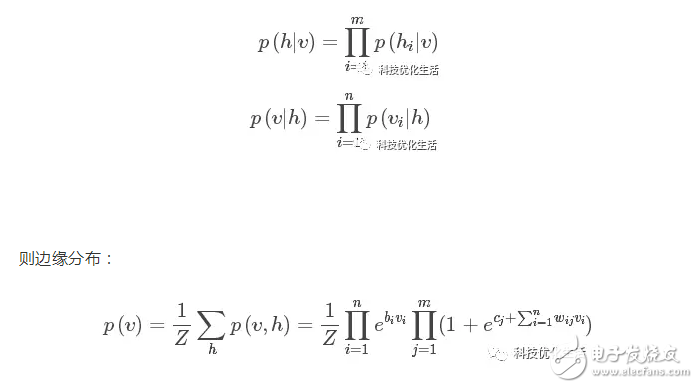
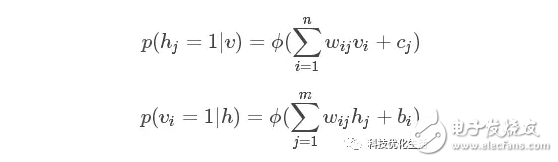There are three main categories of artificial intelligence machine learning: 1) classification; 2) regression; 3) clustering. Today we focus on the Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) algorithm. The restricted Boltzmann machine RBM has always been an important application in the field of deep learning. It is a probability graph model that can be explained by a random neural network. It was proposed by Smolensky on the basis of the Boltzmann machine BM in 1986. A special topology of the Boltzmann machine BM. The Boltzmann machine BM principle originated from statistical physics. It is an energy function-based modeling method that can describe high-order interactions between variables. The learning algorithm of Boltzmann machine BM is more complicated, but it is built. Models and learning algorithms have a relatively complete physical interpretation and strict mathematical statistics theory. RBM concept: Researchers represented by Hinton and Ackley scholars presented BM learning machines with different motivations from different fields. BM is a random recurrent neural network that can be thought of as a randomly generated Hopfield network (see the public domain's artificial intelligence Hopfield network). BM is a symmetrically coupled stochastic feedback binary unit neural network consisting of a visible layer and multiple hidden layers. The network nodes are divided into visible units and hidden units, using visible and hidden units. To express the learning model of the random network and the random environment, through the correlation between the weight expression units. The SBM proposed by Smolensky consists of a visible neuron layer and a hidden neuron layer. Since the hidden layer neurons are not connected to each other and the hidden layer neurons are independent of a given training sample, this allows direct calculation of data-dependent data. The expectation becomes easy, and the visible layer neurons are not connected to each other. The Markov chain sampling process is performed on the hidden layer neuron state obtained from the training samples to estimate the expected value independent of the data, and all visible layers are alternately updated in parallel. The values ​​of neurons and hidden neurons. RBM introduction: The restricted Boltzmann machine RBM simplifies the Boltzmann machine, making the Boltzmann machine BM easier to use. The hidden elements/elements and hidden elements/hidden elements of the Boltzmann machine BM are fully connected, which increases the calculation amount and calculation difficulty, and is difficult to use. RBM, on the other hand, imposes some restrictions on the BM, so that there is no connection between the hidden elements, which greatly reduces the amount of calculation and is very convenient to use. RBM principle: The RBM parameters are as follows: 1) a direct weight matrix Wij of the visible node and the hidden node; 2) The offset of the visible node b = (b1, b2, ..., bn); 3) The offset of the hidden node c = (c1, c2, ..., cm); These parameters determine that the RBM network encodes one n-dimensional sample into one m-dimensional sample. Assuming that the state of the hidden element and the explicit element of the RBM is 1 or 0, its energy function is: According to the Gibbs distribution: p(v,h)=(1/Z)*e[? E(v,h)] and the above energy function establish a joint probability distribution of the model. The visual node state is only affected by m hidden nodes. Similarly, each hidden node is also affected by only n visual nodes. which is: Where Z is a normalization factor or a partition function that represents the (energy index) summation of all possible states of the set of visible and hidden layer nodes. The computational complexity of Z is very high and cannot be directly calculated. Some mathematical derivation is needed to simplify the calculation. Similarly, p(h) is obtained. According to the Bayesian principle, knowing the joint probability and the edge probability, the conditional probability is: Here? Is the sigmoid function. The conditional probability is to determine the state of the explicit or hidden element based on the state of the hidden element or the explicit element, the weight W, the deviation b or c.
Focusing on the development and production of Wireless Charging products that make life easier.
Supply various wireless charger including multifunctional Wireless Charger, Car Wireless Charger, Magnetic Wireless Chargin, Wireless Charging Mouse Pad, etc.
We help 200+ customers create custom wireless charging products design for various industries.
Manufacturing high quality products for customers according to international standards, such as CE ROHS FCC REACH UL SGS BQB etc.
Wireless Charging Pad,Wireless Phone Charger,Wireless Car Charger,Bluetooth Charger TOPNOTCH INTERNATIONAL GROUP LIMITED , https://www.mic11.com