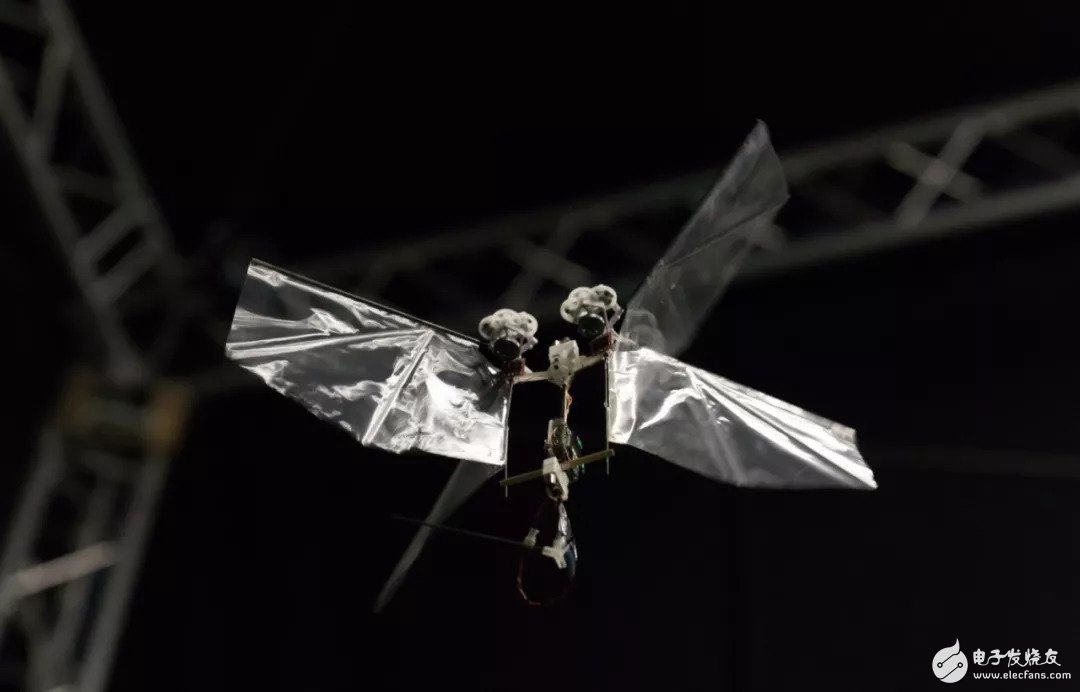
Houseflies or fruit flies have incredible agility, so that all drones and robots are beyond the reach, and now drones are beginning to catch up. A new four-wing flapping-wing robot not only successfully imitates the super-flexible flight mechanism of fruit flies, but also has a maximum flight distance of up to one kilometer on a single charge. Recently, robotics researchers at Delft University of Technology have created a flying platform that seeks to imitate and test the theory of how insects fly, but does not use non-bionic propulsion devices such as propellers. They successfully created a DelFly Nimble flying robot that mimics the flight mechanism of fruit flies. This is not just because they want to build cool robots: insects react quickly to gusts of wind or the hand that is about to be photographed, and their control feedback is incredibly accurate. These characteristics can provide important information worthy of reference for autonomous aircraft such as unmanned aerial vehicles and even small aircraft. Wouldn’t it be great to allow the aircraft to avoid lightning automatically and smoothly? But the trouble is that when the aircraft is much larger than the insect, this way of flying is not always effective due to differences in mass, air resistance, etc. The researchers also mentioned this in their paper, which appeared on the cover of this issue of Science: For the design of flying robots, due to the technical challenges brought about by strict weight and size restrictions, most of the existing design solutions cannot be compared with the flight performance of mimicking organisms. These flying robots have insufficient agility, insufficient take-off ability, or insufficient energy, and the flight time on a single charge is less than one minute. Not only that, small robots like Robobee also need a wired power connection, and other small winged robots need to be driven manually. The DelFly Nimble team does not blindly imitate the bionic characteristics of a certain animal, but focuses on how to achieve similar flying characteristics within the scope of reality. The four-wing tailless DelFly Nimble flying robot built by the team can reach a speed of 7 meters per second (25 kilometers per hour). It can hover in the air or perform various extreme actions, such as diving and rolling in the air. DelFly Nimble uses a rotor with continuous thrust to support coordinated wing movement.
USB 2.0 is a USB interface standard released in 2000 with a theoretical maximum transmission speed of 480Mbps (about 60MB/s). The port has four cables (five cables for MicroUSB and MiniUSB), and the maximum output current is 0.5A. USB 2.0 is currently the most common version of USB port, almost all computers have USB 2.0 port, most USB devices also support USB 2.0. USB 2.0 hub. The device can provide USB high speed or full speed connection on the uplink port. The device also provides USB high-speed, full-speed, or low-speed connections on the downlink port. When the uplink port is connected to an electrical environment that supports only high-speed, full-speed, and low-speed connections, the high-speed, full-speed, and low-speed USB connections on the downlink port are enabled. When the uplink port is connected to an electrical environment that supports only full or low speed connections, the USB high-speed connection on the downlink port is disabled. USB 3.0 Hubs is higher than usb 2.0 in terms of transmitting data.
Usb 2.0 Hubs,7 Port Usb 2.0 Hub,Wireless Usb 2.0 Hub,Usb C To Usb 2.0 Hub Henan Yijiao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.yjusbcable.com