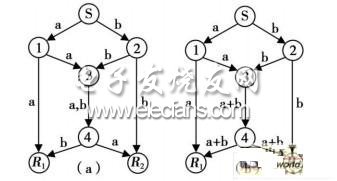
introduction In 2000, Ah ls wede and others first proposed the theory of network coding, which can maximize the network traffic through network coding. In 2003, L, i Yeung, and Cai proved that linear network coding can achieve the maximum flow of the network. Then T. H o et al. Proposed the theory of random network coding. The idea is that the nodes participating in the transmission in the network, the data transmitted on the output channel is a random linear combination of the data transmitted on multiple input channels at that point, and they prove The receiving node can correctly recover the information sent by the source with a high probability. Network coding improves the throughput and reliability of the network, but it also brings security problems that cannot be ignored, including pollution and eavesdropping. THo et al. Proposed a network code that can detect the presence of pollution attacks. Jagg i and others have designed an adaptive secure network code for different attacker capabilities. Sun Yue and others considered the problem of network multicast recovery under network coding. 1 Basic principles of network coding 1.1 Network coding definition The minimum cut theorem of the maximum flow of network information flow: For a known network flow graph, the maximum value of the flow from the source S to the destination T is equal to its minimum cut capacity, that is, m ax fl ow (S, T) = m in C (S, T). For a network with only one sink, the maximum flow can be obtained by routing. In order to deeply understand the theoretical basis of network coding, the following will take the classic butterfly network as an example to illustrate that the use of network coding can make the network communication reach the maximum flow limit. Figure 1 Multicast network with two destination nodes using coding. Figure 1 is a multicast network with a unit capacity of two destination nodes (each side has a capacity of 1). Assume that each link is error-free and delay-free. By the maximum flow minimum cut theorem, m axflo w (s, R l) = 2. At this time, the maximum propagation rate from the source node to the destination nodes R1 and R2 cannot exceed 2. If coding is not used, as shown in Figure 1 (a), the link (3, 4) must send one more bit, which exceeds the capacity of that side. However, if the network flow entering the node is allowed to be encoded, as shown in Fig. 1 (b), a scheme for sending a and b to the destination nodes R 1 and R 2 at the same time is shown. Here, "+" is an exclusive OR operation. In this way, the destination node R1 receives a and a + b, and performs an exclusive OR operation on a and a + b to recover b. Similarly, the destination node R2 can recover a and b. In this way, the butterfly network can obtain the maximum flow limit. 2 Research on the security of network coding in the network Although the original intention of network coding is to improve the throughput of the network, it is also a good way of secure network transmission with further research. However, in actual network communication, there are still hidden security risks, which are mainly manifested in packet pollution and Byzantine attacks in the data forwarding process are common methods and methods of destroying the safe transmission of data. 2.1 Network packet encoding pollution The attack of packet pollution is a common research object in the field of security and is also the most worthy of research. The attacker damages the network nodes and injects new information to form new encoded data packets. Since each node of the network encoding has not only routing functions but also encoding functions Among them, the affected honest node further affects other honest nodes from a damaged packet. This kind of attack can cause pollution to spread on the network like a plague. Obviously, even for some injectable packets, the attacker can reduce their performance. At present, a solution to the anti-packet pollution technology is to use asynchronous high-efficiency linear check code, but this technology has seriously affected the throughput. Malicious packets. The attacker pretends to be an honest node and passes incorrect information to neighbor nodes. This attack results in the original node's information encoding cannot be decoded by the expected next hop node, which affects the correct decoding of downstream nodes. A malicious node may change the message carried in the data packet or the information contained in the header of the data packet, resulting in an error in the header. In a data packet, some important information (such as the global coding core in the network coding, the location of the data packet, the destination of the data packet, etc.) is recorded in the packet header. Any error in the packet header may cause serious transmission problems . If the global coding core changes, it is called a global coding core error, which will affect the decoding of the receiving node; if the destination information is changed, it may cause the receiving node to lose the data packet. According to the classification of La m port and others, most of the above errors can be attributed to Byzantine errors. Portable Solar Power Generator 500w Solar Generator,Emergency Power,Best Portable Power Station,Lifepo4 Power Station suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.nbwhaylan.com