This article discusses the overheating protection of the motor on the risk of overheating. Motors are often used in daily life and work in all walks of life. If you do not take protective measures for the motor, it may cause a safety accident. Motor-driven electrical appliances may present dangers in electric shock, fire, and overheating. There are many reasons for motor overheating, such as overloading operation, inappropriate selection, cooling failure, lack of monitoring and necessary maintenance, which lead to premature insulation aging. The motor will produce losses during operation. These losses on the one hand reduce the efficiency of the motor, on the other hand, the losses are converted into motor heat, which causes the temperature of the motor winding to increase. The service life of the winding insulation material is related to its working temperature. If the temperature is too high, the insulation material will accelerate aging, which will rapidly reduce the insulation performance, greatly shorten the service life of the motor, and even cause fire and electric shock hazards. Therefore, the purpose of motor overheating protection is mainly to adopt protective measures in the design, manufacture, installation and use of the motor. When the motor works under certain load and heat dissipation conditions, the temperature of the winding does not exceed the standard allowable value. Table-1 Comparison table of motor protection measures Table-2 Motor nameplate information Table-3 Comparison of resistance method and thermocouple method Table-4 Maximum winding stall temperature limit
Coupletech Co., Ltd could manufacture and supply a variety of nolinear Optical Crystal ( NLO crysal ), which is Lithium Triborate (LBO) crystal, Potassium Titanyl Phosphatecrystal ( KTP ) crystal, KTA crystal, Beta Barium Borate ( BBO) crystal, BIBO crystal, Lithium niobate ( LiNbO3, LN ) crystal, Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate & Potassium Dideuterium Phosphate (DKDP (KD*P) and KDP ) crystal, periodically poled crystal ( MgO: PPLN, PPLN ) crystal and infrared Nonlinear Optical Crystals ( AgGaS2, ZnGeP2 ) crystal with top quality, unbeatable prices, prompt delivery and the best pre- and post- sales technical support and services, for not only science users but commercial customers and industrial manufacturers all over the world.
Coupletech's NLO crystal is widely used for frequency doubling ( SHG ), third-harmonic generation ( THG ), sum frequency (SFG), optical difference frequency ( DFG ), optical parametric oscillator ( OPO ), and so on.
Nonlinear Optical Crystals,KTP Crystals,BBO Crystals,LBO Crystals,BIBO Crystals,KTA Crystals,LN Crystals,PPLN Crystals Coupletech Co., Ltd. , https://www.coupletech.com
Illustration of motor protection equipment
Relevant standards for motor overheat protection
Each country or each individual standard has different requirements for motor overheat protection. We use Canadian Electrical Code (Canadian Electrical Code, Part I, Safety Standard for Electrical InstallaTIons) and one of the Canadian National Standards (A NaTIonal Standard of Canada ) CAN / CSA-C22.2 NO.68 Motor-Operated Appliances (Household and Commercial) as an example, a brief interpretation of the standard requirements. The above two standards are the standards developed by CSA (Canadian Standards AssociaTIon) and adopted by the Canadian government as national standards.
The classification and usage of the main motor protectors, as shown in Table-1: 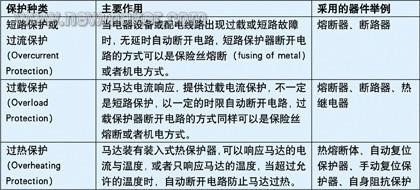
Take Canadian National Standard / CSA Standard CAN / CSA-C22.2 NO.68 as an example to understand how motor-driven electrical appliances can achieve motor overheat protection to meet the requirements of the standard. The standard lists the following ways or possible situations:
(1) Use a motor-mounted thermal protector that complies with CSA Standard C22.2 No. 77 Motor with Inherent OverheaTIng Protection. These motor overheat protectors are listed in the above table. When using, please note that the protector can not only respond to the motor current, but also need to have a proper rated working voltage, current value and temperature predetermined protection value, and the thermal protector needs to be suitable for the motor. The tests required by the standard are Running Heating Temperature test, Locked-Rotor Temperature test and Locked-Rotor Endurance test. If the motor complies with this standard, it can be labeled "THERMALLY PROTECTED". In other words, when the motor complies with the standard CSA68 and the motor standard CSA77, the motor meets the standard requirements under normal operating rated load (Rating), overload (Running Heating) and locked-rotor (Locked-Rotor) application conditions. The motor is protected from overheating.
(2) If the motor-driven electrical appliance is equipped with an overload protection device (Overload Protection device), overheating protection is not necessarily required. In this case, it is necessary to meet the requirements of CEC Part I. This type of overload protector is different from the overheat protector mentioned above. It only depends on the response of the motor current to achieve protection. It can be separate from the motor or attached to the motor. For the selection of tripping current, the ratio of the tripping current of the protector to the rated current of the motor generally does not exceed 1.15. If you choose to use Fuses (fuse) as an overload protector separate from the motor, this type of Fuse requires Time-delay fuse of the type (“D†Fuse).
(3) For some commercial appliances, it is necessary to permanently connect (Permanent Connection) to the building's distribution line. It is not necessary to install an overload protector in the appliance, but it must be ensured that the distribution line provides overload when the appliance is connected. Protection, and appliances need to have a warning label (CAUTION).
(4) For some specific electrical appliances, the standard exempts the motor overheat protector. For example, Momentary Contact Switch (Momentary Contact Switch) is used to control motor electrical appliances, handheld electrical appliances, and household appliances with manned intermittent operation and built-in fuses. In addition, for household appliances that are on duty with intermittent operation, the motor overheat protector can be exempted if it passes the evaluation of the locked rotor test.
Case
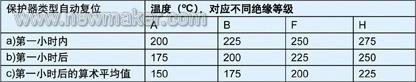
For example, a manufacturer produces air compressors and sells them in North America (Canada and the United States), applying for CSA product safety certification to meet North American standards. The applicable standard of this type of product is CAN / CSA-C22.2 NO.68, in which the motor nameplate information used by the air compressor is extracted as follows: The motor uses CSA certified built-in thermal protector, and the type is automatic reset motor thermal protector (Motor thermal automatic reset protector). As the above thermal protection method, applicable method (1), the motor must meet the CSA standard C22.2 No. 77. The following will give an example of the motor stall temperature test required by this standard: Motor stall temperature test TEMPERATURE) 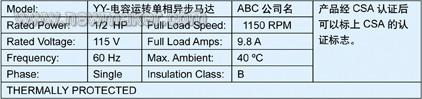
The purpose of the locked-rotation temperature test is to evaluate that the motor runs in the locked-rotation state and the temperature of the winding does not exceed the standard allowable value. The overheat protector can protect the motor from overheating.
2. testing method
According to the standard requirements, the resistance method or the thermocouple method is used to measure the motor stall temperature. In general, the appropriate test method should be selected according to the type of motor or the situation in the laboratory. 
â—† The standard requires type testing, select representative samples (combination of motor and protector) for testing.
â—† Motor samples need to use wood or other thermal insulation materials as fixtures to fix the motor and block the motor shaft.
â—† Unless otherwise specified, the installation position of the motor must make the protector be placed under the maximum, called "Worst Case", because according to the principle of heat conduction convection, the temperature above the winding is usually higher than the temperature below, when the protector is below When tripped, the temperature above the winding will be the highest.
â—† In order to determine the hottest point of the winding temperature, the thermocouple needs to be placed on the actual working winding. In the example, the capacitor running single-phase asynchronous motor must be placed on the actual working main winding. Generally, at least 4 thermocouples, such as Before and after the winding, one point before and after the bottom.
â—† The test voltage of the motor is based on the rated voltage of the nameplate of the motor. Generally, the nominal voltage corresponding to the mains power specified by the standard is selected. For example, the nameplate voltage is 110-120 V, and the test voltage is 120 V. In this example, the motor nameplate voltage is 115 V, then the test voltage is 120 V.
â—† Connect a 3 A fuse in series with the metal shell of the motor to the power ground. If the 3 A fuse blows, you can check that the motor insulation is damaged and the case is live.
â—† The data to be recorded include voltage, frequency, locked rotor current, ambient temperature and continuous winding temperature.
4. Test procedure and result judgment 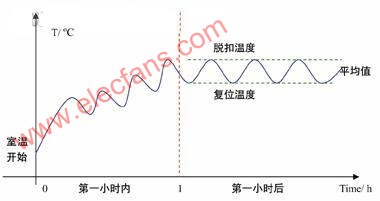
Figure-1 Curve of time and temperature of locked rotor winding (for example, combination of single-phase motor and automatic reset thermal protector)