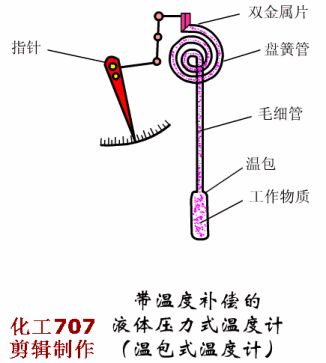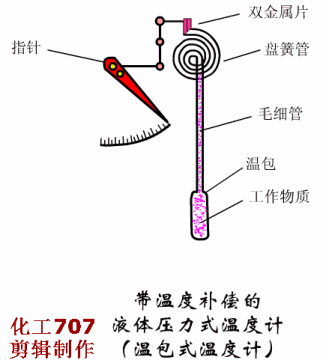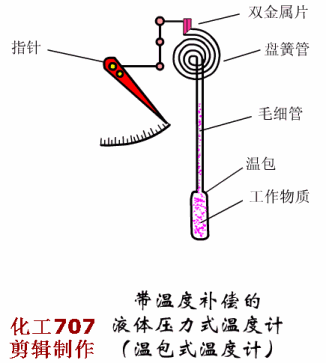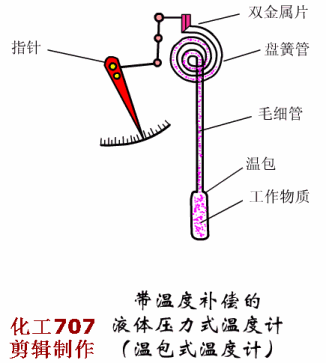
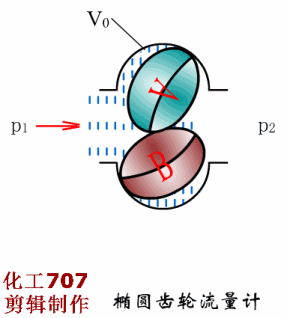
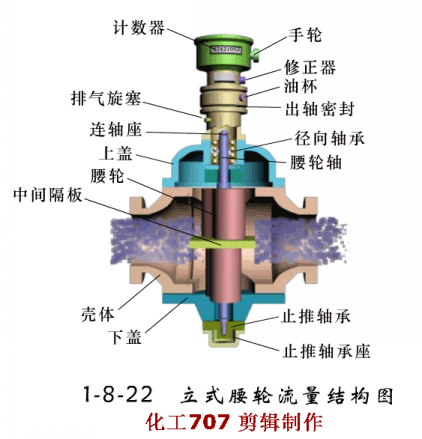
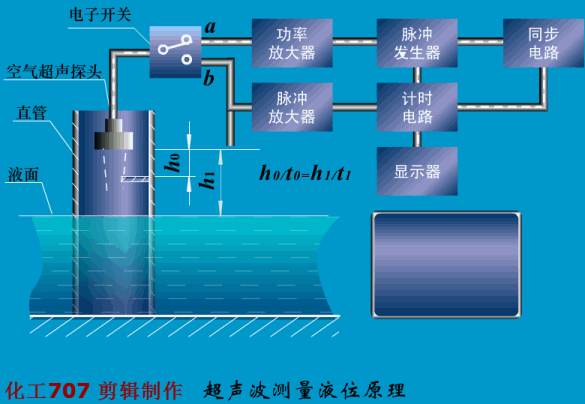
Written in the front: The instrument plays an important role in the detection, display, recording or control of process parameters in the industrial production process. The detection of the process of production is the basic means of understanding and controlling industrial production. Only at all times can the entire process be accurately understood and controlled to ensure a smooth production process and produce with high productivity and low consumption. qualified products. So, don't look at the instrument, but it is the most indispensable! Today, Xiaobian takes everyone to learn the selection of various types of instruments, very comprehensive! Today, we will introduce the selection of automatic instruments, temperature meters, pressure meters, flow meters and level meters. First, the general principle of automatic instrument selection The general principles for the selection of instrumentation (components) and control valves are as follows: 1. Process conditions The temperature, pressure, flow, viscosity, corrosivity, toxicity, pulsation and other factors of the process are the main conditions that determine the selection of the instrument. It is related to the rationality of the instrument selection, the service life of the instrument and the fire prevention, explosion protection, security, etc. of the workshop. problem. 2. The importance of operation The importance of the parameters of each detection point is the basis for selecting the functions of the instrument, such as indication, recording, integration, alarm, control, and remote control. Generally speaking, variables that have little effect on the process, but need to be monitored frequently, can be selected; for important variables that need to be constantly understood, the record should be selected; and some that have a greater impact on the process, The variables to be monitored at any time shall be controlled; for variables that require measurement or economic accounting related to material accounting and power consumption, it is advisable to set up calculations; for some variables that may affect production or safety, alarms should be set. 3. Economic and unity The selection of the instrument is also determined by the scale of the investment. The necessary economic accounting should be carried out under the premise of meeting the requirements of the process and self-control, and the appropriate performance/price ratio should be obtained. In order to facilitate the maintenance and management of the instrument, the uniformity of the instrument should also be noted during the selection. Try to use the same series, the same specification and the same manufacturer's products. 4. Use and supply of instruments The selected instrument should be a relatively mature product, which proves reliable performance through on-site use. At the same time, it should be noted that the selected instrument should be sufficient supply and will not affect the construction progress of the project. Second, the selection of temperature instruments <a> general principle 1 unit and scale (scale) The scale (scale) unit of the temperature meter is uniformly used in Celsius (°C). 2 detection (measuring) component insertion length The selection of the insertion length should be based on the principle that the detection (measuring) component is inserted into the sensitive position of the temperature of the measured medium. However, in general, in order to facilitate the interchange, the entire device is generally selected to have a length of one to two gears. When installing on flue, furnace and masonry equipment with thermal insulation materials, it should be selected according to actual needs. The material of the detection (measuring) component cover should not be lower than the equipment or pipe material. If the shaped product cover is too thin or resistant to corrosion (such as armored thermocouples), a protective sleeve should be added. Explosion-proof type should be used for temperature instruments, temperature switches, temperature detection (measuring) components and transmitters that are installed in flammable and explosive places. <2> Selection of the local temperature meter 1 accuracy level General industrial thermometer: use grade 1.5 or grade 1. Precision measuring and laboratory thermometers: 0.5 or 0.25 should be used. 2 measuring range The highest measured value is not more than 90% of the upper limit of the meter's measuring range, and the normal measured value is about 1/2 of the upper limit of the meter's measuring range. The pressure thermometer should be measured between 1/2 and 3/4 of the upper limit of the meter's measurement range. 3 bimetal thermometer It should be preferred when meeting the requirements of measuring range, working pressure and accuracy. The diameter of the case is generally φ100mm. In places with poor lighting conditions, high position and long viewing distance, φ150mm should be used. The connection between the instrument case and the protection tube should generally be either universal or radial or radial according to the principle of convenient observation. 4 pressure thermometer It is suitable for on-site or on-site display with low temperature below -80 °C, inability to observe at close range, vibration and accuracy. 5 glass thermometer It is only used for special occasions with high precision, low vibration, no mechanical damage and convenient observation. However, due to mercury, it is not advisable to use a mercury thermometer. 6 base instrument For local or local instrumentation measurement and control (adjustment) instruments, base temperature instruments should be used. 7 temperature switch Suitable for occasions where temperature measurement requires contact signal output. <3> Selection of 1 centralized temperature meter (detection) component (1) According to the temperature measurement range, select the thermocouple, thermistor or the thermistor of the corresponding index number. (2) Thermocouples are suitable for general use. Thermal resistance is suitable for vibration-free applications. Thermistors are suitable for applications where fast response times are required. (3) According to the measurement object's response speed requirements, the following time constant detection (measurement) components can be selected: Thermocouple: 600s, 100s and 20s; Thermal resistance: 90 ~ 180s, 30 ~ 90s, 10 ~ 30s and <10s four; Thermistor: <1s. (4) According to the environmental conditions used, select the junction box according to the following principles: Ordinary: a place with good conditions; Splashproof, waterproof: wet or open space; Explosion-proof type: flammable and explosive place; Socket type: only for special occasions. (5) In general, the thread connection method can be selected. For the following occasions, the flange connection method should be used: Installation on equipment, lining pipes and non-ferrous metal pipes; Crystallization, crusting, clogging and highly corrosive media: Flammable, explosive and highly toxic medium. (6) Thermocouples and thermal resistors used in special occasions: For the case of a reducing gas, an inert gas and a vacuum having a temperature higher than 870 ° C and a hydrogen content of more than 5%, a tungsten-rhenium thermocouple or a blowing thermocouple is used; Surface temperature of equipment, pipe outer wall and rotating body, surface or armored thermocouple, thermal resistance; Hard solid particle medium, wear-resistant thermocouple; In the same detection (measuring) component protection sleeve, when multiple temperature measurement is required, a multi-point (branch) thermocouple is selected; An armored thermocouple can be used to save special protection tube material (such as é’½), to improve response speed, or to require the detection (measuring) component to be bent. 2 transmitter The transmitter is selected for measurement or control systems that are compatible with standard signal display instruments. In the case of meeting the design requirements, it is recommended to use a transmitter that integrates measurement and transmission. 3 display instrument (1) The general indicator should be selected for single point display, and the digital indicator should be used for multi-point display. For historical data, it is advisable to use general recorder. (2) Signal alarm system, it is advisable to use a pointer or recorder with contact signal output. (3) A multi-point record should use a medium-sized recorder (such as a 30-point recorder). 4 selection of ancillary equipment (1) When multiple display devices are shared by multiple points, a reliable quality switch should be used. (2) Using a thermocouple to measure the temperature below 1600 °C, when the temperature of the cold junction changes the measurement system can not meet the accuracy requirements, and the supporting display instrument has no cold junction temperature automatic compensation function, the cold end temperature automatic compensator should be used. (3) Compensation wire a. According to the number of thermocouples, the index number and the environmental conditions of use, the compensation wire or compensation cable that meets the requirements should be selected. b. Select different levels of compensation wire or compensation cable according to the ambient temperature: -20~+100°C select ordinary grade; -40~+250°C selects heat resistant grade. c. Where there is intermittent electric heating or strong electric or magnetic field, shield compensation wire or shield compensation cable should be used. d. The cross-sectional area of ​​the compensation wire shall be determined according to the value of the reciprocating resistance of the laying length and the external display resistance of the instrument, transmitter or computer interface. Third, the selection of pressure gauge <a> the choice of pressure gauge 1 according to the use of the environment and the nature of the measured medium (1) In the occasions where the atmosphere is corrosive, dust is high, and the liquid is easy to spray, the closed plastic pressure gauge should be used. (2) Dilute nitric acid, acetic acid, ammonia and other general corrosive media, should use acid pressure gauge, ammonia pressure gauge or stainless steel diaphragm pressure gauge. (3) Dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrochloric acid gas, heavy oil and similar media with strong corrosive, solid particles, viscous liquid, etc., should use diaphragm pressure gauge or diaphragm pressure gauge. The material of the diaphragm or diaphragm must be selected according to the characteristics of the measuring medium. (4) For crystallization, crusting and high viscosity media, diaphragm pressure gauges should be used. (5) In the case of strong mechanical vibration, a seismic pressure gauge or a marine pressure gauge should be used. (6) In the case of flammable or explosive, if an electric contact signal is required, an explosion-proof electric contact pressure gauge should be used. (7) The following measuring media should use a special pressure gauge: Gas ammonia, liquid ammonia: ammonia pressure gauge, vacuum gauge, pressure vacuum gauge; Oxygen: oxygen pressure gauge; Hydrogen: hydrogen pressure gauge; Chlorine gas: chlorine pressure gauge, pressure vacuum gauge; Acetylene: acetylene pressure gauge; Hydrogen sulfide: sulfur-resistant pressure gauge; Lye: alkali pressure gauge, pressure vacuum gauge. 2 accuracy level selection (1) For pressure gauges, bellows pressure gauges and diaphragm pressure gauges for general measurement, 1.5 or 2.5 grades should be used. (2) For pressure gauges for precision measurement and calibration, 0.4, 0.25 or 0.16 should be used. 3 choice of size (1) Pressure gauges installed on pipes and equipment, nominal diameter φ100mm or φ150mm. (2) The pressure gauge installed on the instrument pneumatic pipeline and its auxiliary equipment has a nominal diameter of φ60mm. (3) Install a pressure gauge with low illumination, high position and difficult indication. The nominal diameter is φ200mm or φ250mm. 4 measurement range selection (1) When measuring a stable pressure, the normal operating pressure value should be 2/3 to 1/3 of the upper limit of the meter's measuring range. (2) When measuring the pulsating pressure (such as the pressure at the outlet of the pump, compressor and fan), the normal operating pressure value should be 1/2 to 1/3 of the upper limit of the measuring range of the meter. (3) When measuring high and medium pressure (greater than 4MPa), the normal operating pressure value should not exceed 1/2 of the upper limit of the meter's measuring range. 5 units and scale (scale) (1) The pressure gauge will always use the legal unit of measurement. Namely: Pa (Pa), kilopascal (kPa) and MPa (MPa). (2) For foreign-related design projects and imported instruments, international common standards or corresponding national standards may be adopted. <2>Transmitter, sensor selection (1) When transmitting with standard signal (4~20mA), the transmitter should be selected. (2) For flammable and explosive occasions, pneumatic transmitters or explosion-proof electric transmitters should be used. (3) For crystallization, crusting, clogging, viscous and corrosive media, flange type transmitters should be used. Materials that are in direct contact with the media must be selected based on the characteristics of the media. (4) Resistive or inductive remote pressure gauges or Hall pressure transmitters may be used where the use environment is good, measurement accuracy and reliability are not high. (5) When measuring small pressure (less than 500Pa), a differential pressure transmitter can be selected. <3> Selection of installation accessories (1) When measuring water vapor and medium with a temperature greater than 60 °C, a spiral or U-shaped elbow should be used. (2) When measuring the gas that is easy to liquefy, if the pressure point is higher than the meter, the separator should be used. (3) When measuring dust-containing gas, a dust collector should be used. (4) When measuring the pulsating pressure, a damper or a damper should be used. (5) When the ambient temperature is close to or lower than the freezing point or freezing point of the measuring medium, heat insulation or heat tracing measures should be taken. (6) Instrument protection (warm) box should be selected for the following occasions. Open-air pressure switches and transmitters. Pressure switches and transmitters installed in plants with severe atmospheric corrosion, dust and other hazardous materials. Fourth, the selection of flow meters <a> general principle 1 scale selection The scale of the meter should meet the requirements of the meter scale module. When the scale reading is not an integer, it is convenient for the reading. It can also be selected as an integer. (1) Square root scale range The maximum flow rate does not exceed 95% of the full scale; The normal flow rate is 70% to 85% of the full scale; The minimum flow is not less than 30% of full scale. (2) Linear scale range The maximum flow rate does not exceed 90% of the full scale; The normal flow rate is 50% to 70% of the full scale; The minimum flow is not less than 10% of full scale. 2 meter accuracy The flowmeter used for energy metering shall comply with the provisions of the General Rules for the Provision and Management of Energy Metering Appliances (Trial). (1) For the measurement of fuel into the factory settlement, ±0.1%; (2) Measurement of technical and economic analysis for workshop teams and processes, ±0.5%~2%; (3) For the measurement of industrial and domestic water, ± 2.5%; (4) for steam measurement including superheated steam and saturated steam, ± 2.5%; (5) For the measurement of natural gas, gas and domestic gas, ±2.0%; (6) Measurement of oil used for key energy-using equipment and process control, ±1.5%; (7) Measurement of other energetic working fluids (such as compressed air, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, water, etc.) used for process control, ± 2%. 3 flow units Volume flow rate is m3/h, l/h; Mass flow rate is kg/h, t/h; The gas volume flow rate under standard conditions is Nm3/h (0 ° C, 0.1013 MPa). <2>Selection of general fluid, liquid and steam flow measuring instruments 1 differential pressure flowmeter (1) Throttling device 1 standard throttle device For general fluid flow measurement, standard throttling devices (standard orifices, standard nozzles) should be used. The selection of the standard throttling device must comply with the provisions of GB2624-8l or the international standard ISO 5167-1980. If there are new national standards, the new regulations should be implemented. 2 non-standard throttling device The venturi can be selected if the following conditions are met: Requires accurate measurement at low pressure loss; The measured medium is a clean gas or liquid; The inner diameter of the pipe is in the range of 100 to 800 mm; The fluid pressure is within 1.0 MPa. Double orifice plates are available if the following conditions are met: The measured medium is clean gas or liquid; The Reynolds number is greater than (equal to) 3000, less than (equal to) 300,000. 1/4 round nozzles are available if the following conditions are met: The measured medium is clean gas or liquid; The Reynolds number is greater than 200 and less than 100,000. If you meet the following conditions, you can choose the round hole plate: Dirty medium (such as blast furnace gas, mud, etc.) where the measured medium may produce sediment before and after the orifice plate; Must have a horizontal or inclined pipe. 3 selection of pressure method It should be considered that the entire project should adopt a uniform pressure-taking method. Generally, the angle is used for pressure or flange pressure. According to the use conditions and measurement requirements, other pressure-taking methods such as span pressure can be used. (2) Selection of differential pressure range of differential pressure transmitter The selection of the differential pressure range should be determined according to the calculation. Generally, it should be selected according to the working pressure of the fluid: Low differential pressure: 6kPa, 10kPa; Medium differential pressure: 16kPa, 25kPa; High differential pressure: 40 kPa, 60 kPa. (3) Measures to improve measurement accuracy For fluids with large fluctuations in temperature and pressure, temperature and pressure compensation measures should be considered; When the length of the straight pipe section is insufficient or a swirling flow occurs in the pipe, the fluid correcting measures should be considered to increase the rectifier of the corresponding pipe diameter. (4) Special type differential pressure flowmeter 1 steam flow meter The flow rate of saturated steam can be used when the required accuracy is not higher than 2.5 and is calculated for local or remote transmission. 2 built-in orifice plate flowmeter The small flow rate of clean liquid, steam and gas without suspended matter is measured. The equivalent range ratio is not more than 3:1, and the measurement accuracy is not high. When the pipe diameter is DN<50mm, the built-in orifice flowmeter can be selected. When measuring steam, the steam temperature is not more than 120 °C. 2 area flowmeter Rotor flowmeters are available when the required accuracy is not higher than 1.5 and the turndown ratio is not greater than 10:1. (1) Glass rotor flowmeter Glass rotor flowmeters can be used for local indications of medium to small flow rates, small flow rates, pressures less than 1 MPa, clean, transparent, non-toxic, non-flammable and explosive at temperatures below 100 °C, and non-corrosive and non-adherent to fluid flow. (2) Metal tube rotameter 1 ordinary metal tube rotameter For small flow measurements in fluids that are easily vaporized, condensable, toxic, flammable, explosive, non-magnetic, fibrous, and abrasive, and non-corrosive to stainless steel (1Crl8Ni9Ti), when local or remote signals are required, A common type of metal tube rotameter can be used. 2 special type metal tube rotameter Metal tube rotameter with jacket When the measured medium is easy to crystallize or vaporize or high viscosity, a jacketed metal tube rotameter can be used. A heating or cooling medium is passed through the jacket. Anticorrosive metal tube rotameter For the measurement of corrosive medium flow, an anti-corrosion metal tube rotameter can be used. (3) Rotameter Vertical installation is required with an inclination of no more than 5°. The fluid should be from bottom to top, the installation position should be small, easy to observe and maintain, and the upstream and downstream shut-off valves and bypass valves should be provided. For dirty media, a filter must be installed at the inlet of the flow meter. 3 speed flow meter (1) Target flow meter A liquid flow rate measurement with a high viscosity and a small amount of solid particles. When the required accuracy is not higher than 1.5 and the range ratio is not more than 3:1, a target flow meter can be used. Target flow meters are typically mounted on horizontal pipes. The length of the front straight pipe section is 15 to 40D, and the length of the rear straight pipe section is 5D. (2) Turbine flowmeter The flow rate of clean gas with a clean gas and a kinematic viscosity of not more than 5 × 10 -6 m 2 / s. When a more precise measurement is required and the turndown ratio is not more than 10:1, a turbine flow meter can be used. The turbine flowmeter should be installed on a horizontal pipe so that the liquid fills the entire pipe, and the upstream and downstream shut-off valves and bypass valves are provided, as well as the upstream filter and the discharge valve downstream. Straight pipe length: no less than 20D upstream and no less than 5D downstream. (3) Vortex flowmeter (Kamen vortex flowmeter or vortex flowmeter) Large and medium flow measurement of clean gas, steam and liquid, optional vortex flowmeter. For low-speed fluids and liquids with a viscosity greater than 20×10-3pa·s, it is not advisable to use a vortex flowmeter. The pipe flow rate should be checked when selecting. The flowmeter has the characteristics of small pressure loss and convenient installation. For straight pipe requirements: upstream is 15 ~ 40D (depending on the piping situation); upstream plus rectifier, upstream is not less than 10D; downstream is at least 5D. (4) Water meter When the flow rate of accumulated water in the field is less than 30:1, the water meter can be used. The water meter is installed on the horizontal pipe, and the length of the straight pipe section is required to be: no less than 8D upstream and no less than 5D downstream. <3> Corrosion, Conductive or Solid Particle Flow Measurement Instrument Selection 1 Electromagnetic Flowmeter For liquid or uniform liquid-solid two-phase media flow measurement with conductivity greater than 10 μS/cm. Has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance, no pressure loss. Can measure a variety of strong acid, alkali, salt, ammonia, mud, pulp, pulp and other media. The installation direction can be vertical, horizontal or inclined. When installing vertically, the liquid must be from bottom to top. For liquid-solid two-phase media, it is best to install vertically. When installed on a horizontal pipe, the liquid should be filled with the pipe section, and the electrodes of the transmitter should be at the same level; the length of the straight pipe section is not less than 5~10D upstream, and the downstream is not less than 3~5D or no requirement. Different, different requirements). The transmitter should not be placed in a location where the magnetic field strength is greater than 398 A/m. <4> Selection of high viscosity fluid flow measuring instrument 1 volumetric flowmeter (1) Oval gear flowmeter A clean, high viscosity liquid requires a more accurate flow measurement. When the equivalence ratio is less than 10:1, an elliptical gear flow meter can be used. The elliptical gear flowmeter shall be installed on the horizontal pipe with the indicating dial surface in a vertical plane; the upper and lower shut-off valves and bypass valves shall be provided. A filter should be provided upstream. For micro flow, a miniature oval gear flow meter can be used. When measuring various easily gasification media, a deaerator should be added. (2) waist wheel flowmeter Clean gas or liquid, especially lubricated oil, high accuracy flow measurement, optional waist wheel flow meter. The flowmeter should be installed horizontally, with a bypass line and a filter at the inlet end. (3) scraper flowmeter Continuous measurement of the flow of liquid in a closed pipe, especially the precise metering of various oils, is available with a squeegee flow meter. The scraper flowmeter should be installed so that the fluid fills the pipe and should be installed horizontally so that the counter number is in the vertical direction. When measuring various oils and requiring accurate metering, a deaerator should be added. 2 target flowmeter A liquid flow rate measurement with a high viscosity and a small amount of solid particles. When the required accuracy is not higher than 1.5 and the range ratio is not more than 3:1, a target flow meter can be used. Target flow meters are typically mounted on horizontal pipes. The length of the front straight pipe section is 15 to 40D, and the length of the rear straight pipe section is 5D. <5> Selection of large-diameter flow measuring instruments When the pipe diameter is large, the pressure loss has a significant effect on energy consumption. The conventional flowmeter is expensive, and when the pressure loss is large, the flute-shaped constant velocity tube, the plug-in vortex street, the plug-in turbine, the electromagnetic flowmeter, the venturi tube, and the ultrasonic flowmeter can be selected according to the situation. 1 flute-shaped constant velocity tube flowmeter Flow measurement of clean gas, steam, and clean liquid with a viscosity of less than 0.3 Pa·s. When the required pressure loss is small, a flute-shaped constant velocity tube flowmeter can be selected. The flute-shaped constant velocity pipe is installed on the horizontal pipe. The length of the straight pipe section is not less than 6~24D upstream and not less than 3~4D downstream. <6> Selection of new flow measuring instrument 1 ultrasonic flowmeter Any fluid that can conduct sound can be selected from ultrasonic flowmeters. In addition to general media, media that work under harsh conditions such as strong corrosive, non-conductive, flammable, explosive, and radioactive. When contact measurement cannot be used, Ultrasonic flow meter. 2 mass flow meter Mass flow meters are available for direct and accurate measurement of the mass flow of liquids, high density gases and slurries. Mass flow meters provide accurate and reliable mass flow data regardless of changes in fluid temperature, pressure, density or viscosity. The mass flow meter can be installed in any direction without the need for a straight pipe section. <7> Selection of powder and block solid flow measuring instruments 1 impulse flowmeter Free flow of powder and block solids flow measurement, when it is required to close the transport material, the impulse flow meter should be used; the impulse flow meter is suitable for all kinds of bulk materials of any granularity, and can be accurate in the case of extremely dusty The weight of the bulk material shall not be greater than 5% of the weight of the predetermined punching plate. The installation of the impulse flowmeter requires that the material must be free to fall, and no external force must be applied to the object to be measured. The mounting angle of the punching plate, the angle and height between the feeding port and the punching plate have certain requirements, and have a certain relationship with the range selection. The calculation should be performed before selection. 2 electronic belt scale Solids flow measurement for belt transport on a belt conveyor that meets standard performance. The frame installation requirements are strict, and the position of the frame on the belt and the distance of the drop opening have an influence on the measurement accuracy, and the installation position should be selected. 3 railway scale The continuous automatic weighing of railway wagons should choose dynamic track scale. Fifth, the selection of the level meter <a> general principle (1) The process conditions, the nature of the measured medium, and the requirements of the measurement control system should be deeply understood in order to fully evaluate the technical performance and economic effects of the instrument, so as to ensure stable production, improve product quality, and increase economic benefits. Play the role it deserves. (2) The liquid level and interface measurement should use differential pressure meter, float type meter and float type meter. When the requirements are not met, you can use capacitive, resistive (electrical contact), sonic and other instruments. The surface measurement should be selected according to the particle size of the material, the angle of repose of the material, the conductivity of the material, the structural form of the silo and the measurement requirements. (3) The structure and material of the instrument should be selected according to the characteristics of the medium to be tested. The main considerations are pressure, temperature, corrosivity, conductivity; whether there are polymerization, viscous, precipitation, crystallization, conjunctiva, gasification, foaming, etc.; density and density changes; the amount of suspended matter in the liquid; The degree of surface disturbance and the particle size of the solid material. (4) The display mode and function of the instrument shall be determined according to the requirements of the process operation and system composition. When signal transmission is required, a meter with analog signal output function or digital signal output function can be selected. (5) The meter range should be determined according to the actual display range of the process object or the actual change range. In addition to the level meter for volume measurement, the normal level should generally be about 50% of the meter range. (6) The accuracy of the meter should be selected according to the process requirements, but the level of the meter for volume measurement should be above 0.5. (7) Electronic level meter for explosive atmospheres such as flammable gases, steam and flammable dust. The appropriate type of explosion-proof structure or other protective measures should be selected according to the identified hazard location category and the degree of hazard of the tested medium. (8) For electronic level instruments used in places such as corrosive gases and hazardous dusts, the appropriate enclosure protection type should be selected according to the environmental conditions. <2> Selection of liquid level and interface measuring instruments 1 differential pressure measuring instrument (1) For continuous measurement of liquid level, a differential pressure meter should be used. For interface measurement, a differential pressure gauge can be used, but the total liquid level should always be higher than the upper pressure tap. (2) For the measurement accuracy requirements, the measurement system needs more complicated and precise calculation, and when the general analog instrument is difficult to achieve, the differential pressure type intelligent transmission instrument can be selected, and the accuracy is 0.2 or higher. (3) For the liquid density change under normal working conditions, the differential pressure meter should not be used. (4) Corrosive liquid, crystalline liquid, viscous liquid, easily vaporized liquid, liquid containing suspended solids should use flat flange type differential pressure meter. Highly crystalline liquids, high viscosity liquids, gelled liquids, and precipitating liquids should be selected from plug-in flange differential pressure meters. The liquid level of the above measured medium, if there is a large amount of condensate in the gas phase, precipitates are precipitated, or the high temperature liquid needs to be isolated from the transmitter, or when the measured medium is replaced, the measuring head needs to be strictly cleaned, and the double flange type may be selected. Differential pressure meter. (5) The liquid level of corrosive liquid, viscous liquid, crystalline liquid, molten liquid, and sedimentary liquid can be measured by blowing or flushing when it is difficult to measure with a flange type differential pressure meter. A pressure gauge, a pressure transmitter meter, or a differential pressure transmitter meter is used for measurement. (6) For objects that may condense in the gas phase, may vaporize in the liquid phase, or have liquid separation in the gas phase at ambient temperature, when it is difficult to use a flange type differential pressure meter and measure with a common differential pressure meter, it shall be determined according to the specific conditions. Set up isolator, separator, vaporizer, balance vessel and other components, or heat and heat the measuring pipeline. (7) When measuring the boiler drum level with a differential pressure meter, a temperature-compensated double-chamber balance container should be used. (8) The positive and negative migration of differential pressure gauges should be considered when selecting the meter range. 2 buoy type measuring instrument (1) For the measurement range of 2000mm, the liquid level of the liquid density of 0.5~1.5 is continuously measured, and the measurement range is less than 1200mm, and the liquid interface with the density difference of 0.1~0.5 is continuously measured. The buoy type meter should be selected. For vacuum objects and liquids that are easy to vaporize, float type instruments should be used. Pneumatic buoy type gauges should be used for local level indication or adjustment. Float meters must be used to clean liquids. (2) Select the pontoon type instrument. When the accuracy requirement is high and the signal is required to be transmitted remotely, the force balance type should be selected. When the accuracy requirement is not high, the displacement balance type can be selected when the local indication or adjustment is made. (3) For the liquid level measurement of the open storage tank and the open storage tank, the inner buoy should be selected; for liquid objects that are not crystallized at the operating temperature, are not viscous, but may crystallize or viscous at ambient temperature, The inner buoy should be used. For process equipment that does not allow parking, the inner buoy should not be used, but the outer buoy should be used. For highly viscous, crystalline or high temperature liquid objects, external floatation should not be used. (4) When the inner pontoon meter has a large liquid disturbance in the container, a smooth casing against the disturbance shall be installed. (5) The electric buoy meter is used for occasions where the measured liquid level fluctuates frequently, and the output signal should be damper. 3 float measuring instrument (1) For the continuous measurement and volumetric measurement of the liquid level of the large reservoir cleaning liquid, and the position measurement of the liquid level and interface of the various cleaning tanks, the float type meter should be selected. (2) Dirty liquids, as well as frozen liquids at ambient temperatures, should not be used with float-type instruments. Continuous measurement of viscous liquids and multi-point measurements are not suitable for float gauges. (3) When the float type measuring instrument is used for interface measurement, the specific density of the two liquids should be constant, and the specific density difference should not be less than 0.2. (4) When the inner float type liquid level meter is used for the measurement of the liquid level of the large storage tank, a guiding device should be provided to prevent the float from drifting; in order to prevent the floating body from being affected by the liquid surface disturbance, a smooth casing should be installed. (5) Continuous measurement of liquid level or volume of large storage tank liquid, light storage type liquid level meter should be selected for single storage tank or multiple storage tanks with high measurement accuracy; With a float type liquid level gauge. For single or multiple tanks requiring high precision continuous metering of liquid level, interface, volume and mass, a tank measurement system should be used. (6) The multi-point measurement of the liquid level of the open storage tank and the open storage tank, as well as the multi-point measurement of dangerous liquids such as corrosive and toxic, should be selected as the magnetic float type liquid level gauge. (7) For the position measurement of viscous liquid, a lever type float level controller should be used. 4 capacitive measuring instrument (1) For liquid level continuous measurement and position measurement of corrosive liquids, sedimentary fluids and other chemical process media, a capacitive liquid level meter should be used. For interface measurements, the electrical properties of the two liquids must meet the technical requirements of the product. (2) The specific model, electrode structure type and electrode material of the capacitance liquid level meter should be determined according to the electrical properties of the measured medium and the material of the container. (3) For non-viscous non-conductive liquids, shaft-type electrodes can be used; for non-sticky conductive liquids, sleeve-type electrodes can be used; for non-sticky non-conductive liquids, bare electrodes can be used. The surface of the electrode should be selected to have a low affinity for the liquid to be tested or to be cleaned automatically. (4) Capacitance level gauges cannot be used for continuous measurement of liquid levels of easily viscous conductive liquids. (5) Capacitive measuring instruments are susceptible to electromagnetic interference. Shielded cables should be used or other measures against electromagnetic interference should be adopted. (6) The capacitance level meter used for position measurement should be horizontally mounted; the capacitance level meter used for continuous measurement should be vertical installation type. 5 resistance (electrical contact) measuring instrument (1) For the position measurement of the level of the corrosive conductive liquid, and the interface position measurement of the conductive liquid and the non-conductive liquid, a resistive (electrical contact) meter may be selected. (2) Resistive (electrical contact) instruments are generally not suitable for conductive liquids that tend to foul the electrodes and electrolytic processes between the electrodes. For non-conductive, easy-to-adhere electrodes, resistive (electrical contact) instruments must not be used. 6 static pressure measuring instrument (1) For continuous measurement of the liquid level of water supply tanks, wells and reservoirs with a depth of 5m to 100m, static pressure type gauges should be used. For continuous measurement of the liquid level in a pressureless container, a static pressure meter can be used. (2) Under normal working conditions, when the liquid density changes significantly, static pressure gauges should not be used. 7 acoustic wave measuring instrument (1) Acoustic measuring instruments should be selected for the continuous measurement and position measurement of corrosive liquids, highly viscous liquids, toxic liquids, etc., which are difficult to measure by ordinary level instruments. (2) The specific model and structure type of the acoustic wave instrument should be determined according to the characteristics of the measured medium and other factors. (3) Acoustic meters must be used for liquid level measurement of containers that can reflect and propagate sound waves, and should not be used in vacuum containers. Not suitable for liquids containing bubbles and liquids containing solid particles. (4) Acoustic instrumentation should not be used for containers with internal obstacles that affect sound wave propagation. (5) For the sonic instrument that continuously measures the liquid level, if the temperature and composition of the measured liquid change are significant, compensation for the variation of the acoustic wave propagation velocity should be considered to improve the accuracy of the measurement. (6) Shielded cables should be used for cables between the detector and the converter, or measures against electromagnetic interference should be considered. 8 microwave measuring instrument (1) For the continuous measurement of the liquid level of large fixed top tanks, floating liquids, high viscosity liquids and toxic liquids in the high level of ordinary liquid level instruments, microwave measuring instruments should be used. The microwave measuring instrument measurement method uses microwave continuous scanning in a specific frequency range. When the distance between the liquid level and the antenna changes, a frequency difference, a frequency difference and a distance between the liquid level and the antenna are generated between the sensing signal and the reflected signal. It is proportional, so the measured frequency difference can be converted to the liquid level. (2) The structure and material of the antenna shall be determined according to the characteristics of the measured medium and the pressure inside the tank. (3) For tanks with internal obstacles affecting microwave propagation, microwave type instruments should not be used. (4) When the density of water vapor and hydrocarbon vapor in the tank changes significantly under normal conditions, compensation for changes in microwave propagation velocity should be considered; for boiling or disturbed liquid surfaces, reduction should be considered. The stationary tube of the horn and other compensation measures to improve the measurement accuracy. 9 nuclear radiation measuring instrument (1)对于高温ã€é«˜åŽ‹ã€é«˜ç²˜åº¦ã€å¼ºè…蚀ã€æ˜“爆ã€æœ‰æ¯’介质液é¢çš„éžæŽ¥è§¦å¼è¿žç»æµ‹é‡å’Œä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œåœ¨ä½¿ç”¨å…¶ä»–液ä½ä»ªè¡¨éš¾ä»¥æ»¡è¶³æµ‹é‡è¦æ±‚时,å¯é€‰ç”¨æ ¸è¾å°„å¼ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)è¾å°„æºçš„å¼ºåº¦åº”æ ¹æ®æµ‹é‡è¦æ±‚进行选择,åŒæ—¶åº”使射线通过被测对象åŽï¼Œåœ¨å·¥ä½œçŽ°åœºçš„射线剂é‡åº”å°½é‡å°ï¼Œå®‰å…¨å‰‚é‡æ ‡å‡†åº”符åˆçŽ°è¡Œçš„《è¾å°„防护规定》(GB8703-88),å¦åˆ™ï¼Œåº”充分考虑隔离å±è”½ç‰é˜²æŠ¤æŽªæ–½ã€‚ (3)è¾å°„æºçš„ç§ç±»åº”æ ¹æ®æµ‹é‡è¦æ±‚和被测对象的特点,如被测介质的密度ã€å®¹å™¨çš„å‡ ä½•å½¢çŠ¶ã€æè´¨åŠå£åŽšç‰å› ç´ è¿›è¡Œé€‰æ‹©ã€‚å½“å°„æºå¼ºåº¦è¦æ±‚较å°æ—¶ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨é•ï¼ˆRe);当射æºå¼ºåº¦è¦æ±‚较大时,å¯é€‰ç”¨é“¯137(Csl37);用于厚å£å®¹å™¨è¦æ±‚ç©¿é€èƒ½åŠ›å¼ºæ—¶ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨é’´60(Co60)。 (4)为é¿å…由于è¾å°„æºè¡°å˜è€Œå¼•èµ·çš„测é‡è¯¯å·®ï¼Œæ高è¿è¡Œçš„稳定性和å‡å°‘æ ¡éªŒæ¬¡æ•°ï¼Œæµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨åº”能对衰å˜è¿›è¡Œè¡¥å¿ã€‚ 10激光å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于结构å¤æ‚或有机械障ç¢çš„容器,以åŠæŒ‰å¸¸è§„的方法难以安装的容器的液é¢è¿žç»æµ‹é‡ï¼Œåº”选用激光å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2ï¼‰å¯¹äºŽæ— å射的完全é€æ˜Žæ¶²ä½“,ä¸èƒ½é‡‡ç”¨æ¿€å…‰å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ <三>æ–™é¢æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨çš„选型1电容å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于颗粒状物料和粉粒状物料,如:煤ã€å¡‘æ–™å•ä½“ã€è‚¥æ–™ã€ç ‚åç‰æ–™é¢è¿žç»æµ‹é‡å’Œä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå®œé€‰ç”¨ç”µå®¹å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)检测器的延伸电缆应采用å±è”½ç”µç¼†ï¼Œæˆ–考虑采用防电ç£å¹²æ‰°çš„措施。 2声波å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1ï¼‰å¯¹äºŽæ— æŒ¯åŠ¨æˆ–æŒ¯åŠ¨å°çš„料仓ã€æ–™æ–—内粒度为10mm以下的颗粒物状料é¢çš„ä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨éŸ³å‰æ–™ä½è®¡ã€‚ (2)对于粒度为5mm以下的粉粒状物料的料é¢ä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œåº”选用声阻æ–å¼è¶…声料ä½è®¡ã€‚ (3)对于微粉状物料的料é¢è¿žç»æµ‹é‡å’Œä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå®œé€‰ç”¨åå°„å¼è¶…声料ä½è®¡ã€‚åå°„å¼è¶…声料ä½è®¡ä¸å®œç”¨äºŽæœ‰ç²‰å°˜å¼¥æ¼«çš„料仓ã€æ–™æ–—çš„æ–™é¢æµ‹é‡ï¼Œä¹Ÿä¸å®œç”¨äºŽè¡¨é¢ä¸å¹³æ•´çš„æ–™ä½æµ‹é‡ã€‚ 3电阻å¼ï¼ˆç”µæŽ¥è§¦å¼ï¼‰æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于导电性能良好或导电性能差,但å«æœ‰æ°´ä»½çš„颗粒状和粉粒状物料,如:煤ã€ç„¦ç‚ç‰æ–™é¢çš„ä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨ç”µé˜»å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)必须满足产å“规定的电æžå¯¹åœ°ç”µé˜»çš„数值,以ä¿è¯æµ‹é‡çš„å¯é 性和çµæ•åº¦ã€‚ 4微波å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于高温ã€ç²˜é™„性大ã€è…蚀性大ã€æ¯’性大的å—状ã€é¢—粒状物料的料é¢ä½å¼æµ‹é‡å’Œè¿žç»æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå®œé€‰ç”¨å¾®æ³¢å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)ä¸å®œç”¨äºŽè¡¨é¢ä¸å¹³æ•´çš„æ–™ä½æµ‹é‡ã€‚ 5æ ¸è¾å°„å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于高温ã€é«˜åŽ‹ã€ç²˜é™„性大ã€è…蚀性大ã€æ¯’性大的å—状ã€é¢—粒状ã€ç²‰ç²’状物料的料é¢ä½å¼æµ‹é‡å’Œè¿žç»æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨æ ¸è¾å°„å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)其它è¦æ±‚应符åˆå‰è¿°çš„规定。 6激光å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于结构å¤æ‚或有机械障ç¢çš„容器,以åŠæŒ‰å¸¸è§„的方法难以安装的容器的料é¢è¿žç»æµ‹é‡ï¼Œåº”选用激光å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2ï¼‰å¯¹äºŽæ— å射的完全é€æ˜Žç‰©æ–™ï¼Œä¸èƒ½é‡‡ç”¨æ¿€å…‰å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ 7阻旋å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于承压较å°ã€æ— 脉动压力的料仓ã€æ–™æ–—,物料比密度为0.2以上颗粒状和粉粒状物料料é¢çš„ä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨é˜»æ—‹å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2ï¼‰æ—‹ç¿¼çš„å°ºå¯¸åº”æ ¹æ®ç‰©æ–™çš„比密度选å–。 (3)为é¿å…ç‰©æ–™æ’žå‡»æ—‹ç¿¼é€ æˆä»ªè¡¨è¯¯åŠ¨ä½œï¼Œåº”在旋翼上方设置ä¿æŠ¤æ¿ã€‚ 8隔膜å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于料仓ã€æ–™æ–—内颗粒状或粉粒状物料料é¢çš„ä½å¼æµ‹é‡ï¼Œå¯é€‰ç”¨éš”膜å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)由于隔膜的动作易å—粉粒附ç€çš„å½±å“和粉粒æµåŠ¨åŽ‹åŠ›çš„å½±å“,ä¸èƒ½ç”¨äºŽç²¾åº¦è¦æ±‚较高的场åˆã€‚ 9é‡é”¤å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ (1)对于料ä½é«˜åº¦å¤§ï¼Œå˜åŒ–范围宽的大型料仓ã€æ•£è£…仓库以åŠæ•žå¼€æˆ–密é—æ— åŽ‹å®¹å™¨å†…çš„å—状ã€é¢—粒状和附ç€æ€§ä¸å¤§çš„粉粒状物料的料é¢å®šæ—¶è¿žç»æµ‹é‡ï¼Œåº”选用é‡é”¤å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ (2)é‡é”¤çš„å½¢å¼åº”æ ¹æ®ç‰©æ–™çš„粒度ã€å¹²æ¹¿åº¦ç‰å› ç´ é€‰å–。 (3)对于有粉尘弥漫严é‡çš„料仓ã€å®¹å™¨çš„æ–™ä½æµ‹é‡ï¼Œåº”使用带å¹æ°”装置的é‡é”¤å¼æµ‹é‡ä»ªè¡¨ã€‚ Portable Outdoor Power,Outdoor Power Bank,Outdoor Battery Bank,Outdoor Portable Power SUZHOU DEVELPOWER ENERGY EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.fisoph-power.com