Our company is specialized in supplying Manifold Gauge.We have gauges for all common refrigerant like R22,R134A,R410A,R404A,R407C,R32,R1234YF.It applies to wide range of applications, like installation and maintenance of household air conditioner,automobile air conditioner,refrigerator,cold room and other industries .OEM and customization is welcomed.Our parts have been exported to over 50 countries all over the world and are always got good comment by customers. Manifold Gauge Manifold Gauge,Manifold Gauge Set,Ac Manifold Gauge Set,Ac Manifold Gauges ZHEJIANG ICE LOONG ENVIRONMENTAL SCI-TECH CO.,LTD. , https://www.china-refrigerantgas.com
Keywords: Home Network Sharing Wireless Access Protocol HomeRF Technology
1 Introduction In order to solve the problem of interconnection between consumer electronic devices (such as PCs, video phones, cordless phones, PDAs, etc.) and enable them to share information, various home network technologies have emerged.
At present, the most eye-catching home network technologies are HomeRF, Bluetooth, IEEE802.11 (b) and HomePAN. Sponsored by ITU, with the participation of several major companies such as Compaq, Intel, Philips, HP, IBM, and Microsoft, the HomeRF working group is committed to digital communication between PCs and other household appliances from different countries and different manufacturers. The shared wireless access protocol (Share Wirle SS Access Protocol, SWAP) developed by it combines the characteristics of DECT and IEEE802.11, provides support for voice and data services, and is very suitable for networking in the home environment.
2 HomeRF technology HomeRF's SWAP protocol model is shown in Figure 1. The protocol level has a certain mapping relationship with the OSI network model, but it is not a one-to-one correspondence. In SWAP, MAC (Media Access Layer) corresponds to the data link layer, and the protocol layer above it differs according to the business carried out. It uses TCP / IP to carry data services and UDP / IP to carry streaming services (such as Video data stream, etc.) At the same time, in order to provide high-quality voice services, DECT protocol is also integrated. 
2. The physical layer HomeRF works in the 2.4GHz frequency band, it uses digital frequency hopping spread spectrum technology, the rate is 50 hops / s, and there are 75 frequency hopping channels with a bandwidth of 1MHz. The modulation method is FSK modulation with constant envelope, which is divided into 2FSK and 4FSK. Using FM modulation can effectively suppress interference and fading in the wireless environment.
In 2FSK mode, the maximum data transmission rate is 1Mb / s, and in 4FSK mode, the rate can reach 2Mb / s. In the latest version of HomeRF2.x, WBFH (Wide BandFrequency Hopping) technology is used to increase the frequency hopping bandwidth, from the original 1MHz to 3MHz, 5MHz, the frequency hopping rate is also increased to 75 hops / s, of course, the peak data is 10Mb / s, which is close to 11Mb / s of IEEE802.11b standard, can meet the future home broadband communication. It can dynamically adjust the frequency hopping bandwidth according to the data transmission rate. When the transmission rate is low (<2Mb / s), the bandwidth of 1MHz is used. When the rate is 10Mb / s, the bandwidth of 5MHz is used for communication, as shown in Figure 2. Show. 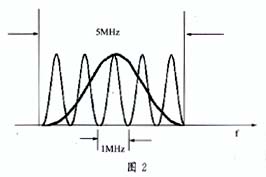
The power consumption of the SWAP system is very low, 100mPW can cover a range of about 40 meters, and can achieve seamless coverage of general user rooms and gardens.
2.2 Media Access Layer (MAC)
The MAC layer of SWAP is equivalent to the data link layer in the OSI model, so its function is mainly to complete the encapsulation and decapsulation of data frames.
As shown in Figure 3, HomeRF spends most of its time on a frequency hopping point for data communication. At the same time, according to the number of active voice channels, it dynamically reserves a part of resources for voice services, which is consistent with the future of home communications based on data Development trend. In order to meet the requirements of real-time communication, SWAP defines a high-level priority for streaming services (Stream Meadia), which can occupy channel resources at any time. For lost voice data packets, SWAP will retransmit at the beginning of the next frequency hopping point. 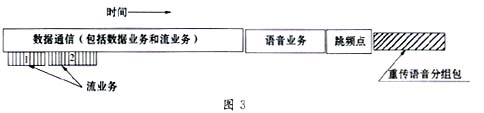
For data communication, SWAP adopts the CSMA / CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) method in IEEE802.11, and the voice service uses the TDMA method based on the DECT system.
SWAP defines two types of frame structures, one is a 20ms superframe (Superframe), the other is a 10ms subframe (Subfram e), these two frames are used in different occasions. Referring to Figure 4 (a), when there are only data services in the network, HomeRF will use superframes, the communication time at a frequency hopping point is 20ms, and adopts asynchronous mode, when there is voice service in the network, the 10ms sub Frame, and added a flag bit (B flag in Figure 4) to communicate in a synchronous manner. Figure 4 describes the changes in the frame structure when voice and data communications are performed simultaneously. 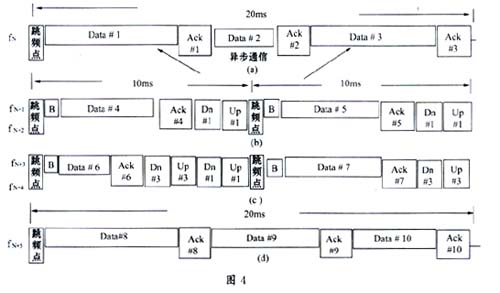
2.3 Network layer As shown in Figure 1, SWAP uses the Internet's TCP / IP protocol, TCP protocol is used for general data communication, and UDP protocol is used to carry out stream business (Stream Media).
The form of SWAP networking is very flexible. It can use either ad-hoc network or control network. In an ad-hoc structured network, all access points are equal, either as a host or as a router, and distributed control of the network by each point, but this network structure only supports data communication. For services that require time (such as voice communication, etc.), a control network must be used. At this time, a special control point (Control Point, CP) must be used to manage and coordinate the entire system. If the USB is connected to a PC, it can become a gateway to the PSTN. At the same time, a power management module is added to this CP point to rationally arrange the wake-up and polling time of various devices in the network to extend the battery life. .
In SWAP, a subnet has a 24-bit ID number and can accommodate up to 256 access devices. These access devices are mainly divided into four types:
· Connection point (ConnecTIon Point), equivalent to the control point CP, can support voice and data communication.
· Voice terminal equipment adopts TDMA mode for voice communication.
· Data node equipment adopts CSMA / CA mode for data communication.
· Other node devices that can support both voice and data services.
HomeRF1. The terminal of x can actually achieve real roaming, but there is no detailed description of the problems of handover and multi-address conflict in the standard protocol. The new version of HomeRF2.0 protocol describes the roaming mechanism in a standardized manner, which can realize the seamless switching of the terminal between adjacent access points.
2.4 Voice Communication In order to provide high-quality voice communication, HomeRF inherits the protocol and specifications of the currently very successful cordless telephone system-DECT.
The voice quality of HomeRF2.0 can reach 4.1 MOS, while the quality of general public phones is 4.3 MOS, and the voice quality of mobile phones is only 3.4 MOS. Based on DECT, HomeRF can continue to support various new services, such as call waiting and call forwarding. The system can accommodate up to 8 active voice channels.
2. The 4GHz ISM frequency band is a frequency band that is open to the whole world and is widely used in scientific research, industry, and medical systems. This frequency band can be used by almost all countries, enterprises, and individuals without applying, so the wireless communication system working in this frequency band Unpredictable sources of interference will be encountered, such as certain home appliances, cordless phones, other wireless LANs, microwave ovens, etc. These interferences will cause packet loss. To solve this problem, HomeRF uses a retransmission mechanism, as shown in the figure As shown in 5, at the frequency point fN, the voice data packet is lost due to external interference, so the CP control point (ControlPoint) arranges for retransmission in the next frequency point within 10ms. 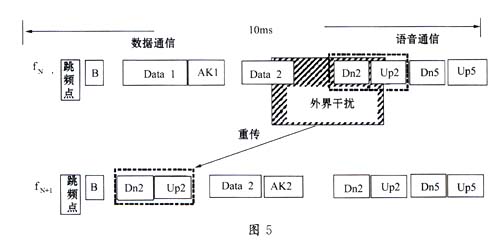
2.5 Data Communication and Streaming Service (Stream Media)
In order to achieve efficient transmission of data packets, HomeRF adopts the CSMA / CA mode in the IEEE802.11 standard, which is similar to CSMA / CD, and obtains control of the channel in a competitive manner. There can only be one at a time. An access point transmits data on the network.
Unlike other protocols, HomeRF provides real support for streaming services (Stream Media). Since the streaming service stipulates a high level of priority and adopts a retransmission mechanism with priority, this ensures the bandwidth and low interference and low bit error required by the real-time streaming service. SWAP can support up to 8 active streaming service channels at the same time. These streaming services can use simplex, duplex and multicast methods.
Typical applications for streaming services are interactive video conferencing, wireless headsets, Dolby surround sound, etc.
2.6 Random frequency hopping and low power transmission of the security mechanism can effectively prevent malicious attacks on the system and data interception by the outside world. HomeRF uses the Blowfish encryption algorithm (with up to 1 trillion codewords) for the data, further increasing the security of the data.
3 Comparison with other home network protocols Home networks are mainly divided into two categories: wired networks and wireless networks. Wired networks mainly use telephone lines or power lines in the home for networking; wireless networks mainly use wireless resources in the 2.4 GHz frequency band for networking.
3.1 Wired networking
3.1.1 Phone Line Networking The HPNA organization (Home Phoneline Networking Alliance) has developed standards for implementing home networks on existing phone lines. There are two versions, 1.0 and 2.0, of which HPNA1.0 supports 1Mbps. Transmission rate, and HPNA2.0 can reach 2Mbps.
HomePNA uses frequency division multiplexing technology to carry multiple services on existing telephone lines without mutual interference, and different services are allocated to different frequency bands. HomePNA is simple to use, easy to maintain, has a more suitable price / performance ratio, supports Internet access, and supports interface V. 90. ADSL and Cable Modem, and it can be used together with Ethernet or HomeRF.
3.1.2 Power line networking The existing power lines in the home can also be used for networking. Enikia, Intellon and Intelogis are working in this area. The data is encrypted before transmission, and the signal decays faster, thereby ensuring security. But power lines have their flaws: they are susceptible to interference such as lightning, and lightning can also threaten equipment. Currently, power line networks support the Ethernet standard, so the software between them can be used universally. 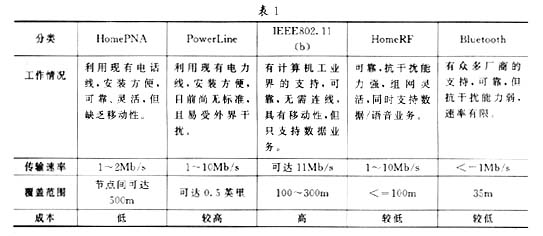
3.2 The most ideal technology for wireless networking to connect home networks is wireless communication technology. At present, there are mainly three types of home wireless networking technologies: IEEE802.11 (wireless local area network), HomeRF and Bluetooth technology.
3.2.1 IEEE802.11 standard IEEE802.11 is a wireless local area network standard, which mainly defines the specifications of the physical layer and the MAC layer. At the physical layer, it supports infrared, FHSS frequency hopping spread spectrum and DSSS direct spreading. The MAC layer uses the CSMA / CA carrier sense multiple access / collision avoidance (Carrier Sense MulTI ple Access with Collision Avoidance) protocol. 802.11a and 802.11b are two extended standards. 802.11a works in the 5GHz frequency band and the transmission rate is up to 54Mb / s, while 802.11b working in the 2.4GHz frequency band is suitable for the home environment. / S.
However, compared with HomeRF, IEEE802.11 products are too expensive, and currently only support data communication.
3.2.2 Bluetooth technology The Bluetooth project was initiated by Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, Toshiba and other five companies. Its goal is to provide a universal wireless interface standard to replace the intricate cables in traditional networks with microwaves. Realize convenient and fast, flexible and safe, low-cost and low-power data and voice communication.
The working frequency band of Bluetooth is 2.45 GHz, which is available all over the world. Frequency-hopping communication is carried out at a rate of 1600 hops / s. With 2.45 GHz as the center frequency, 79 frequency points are selected and the channel bandwidth is 1 MHz. When the transmission bandwidth is 1MHz, its effective data rate is 721 kbit / s, and the communication range is about 10 meters. The Bluetooth standard protocol stack uses a layered structure to complete the filtering and transmission of data streams, frequency hopping and data frame transmission, connection establishment and release, link control, data disassembly, quality of service (QoS), and protocol replication Use and share functions.
At present, Bluetooth technology is supported by many manufacturers, but its communication quality in the home environment is still not ideal. Compared with HomeRF, the anti-interference ability is not strong, and the data rate drops rapidly after being interfered.
In general, IEEE802.11 is more suitable for wireless networks in commercial environments, Bluetooth technology is suitable for interconnection between mobile devices, and HomeRF is suitable for communication in the home environment. Table 1 compares the characteristics of these technologies.
4 Conclusion HomeRF is different from other technologies in that it is positioned from the beginning to build a home network, fully considering various factors in the home environment, so it is suitable for future broadband communication for homes.
In the next few years, the average annual growth rate of the home network will reach 95%, and the use of wireless technology will increase year by year. HomeRF technology has been recognized by users for its good cost performance.
Home Broadband Network Based on HomeRF
ã€Abstract】 The principle and mechanism of HomeRF technology are discussed, and compared with several other home network technologies.
references
1 Kevin J Negus. Overview of the HomeRF. http: // www. HomeRF. org